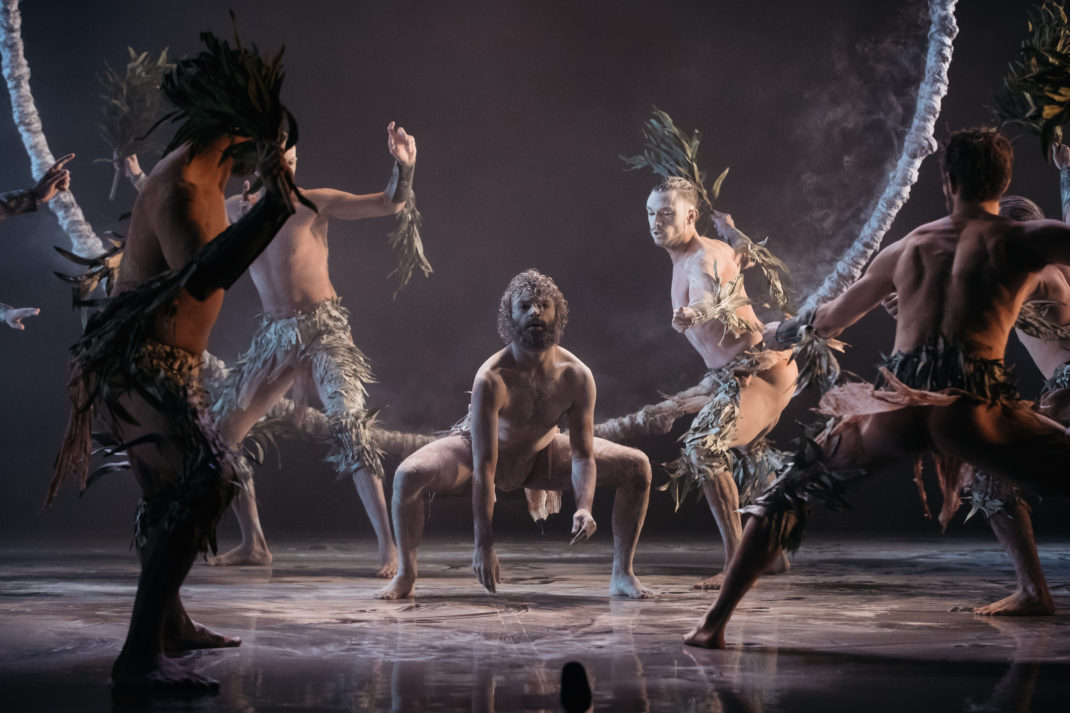16 January 2024. Neilson Studio, Walsh Bay. Sydney Festival
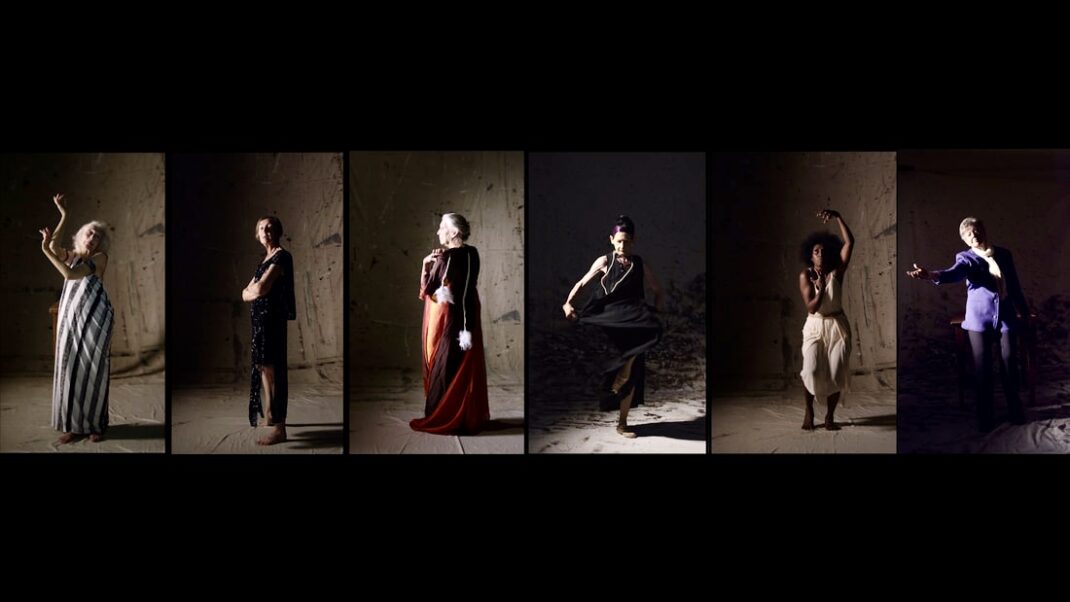
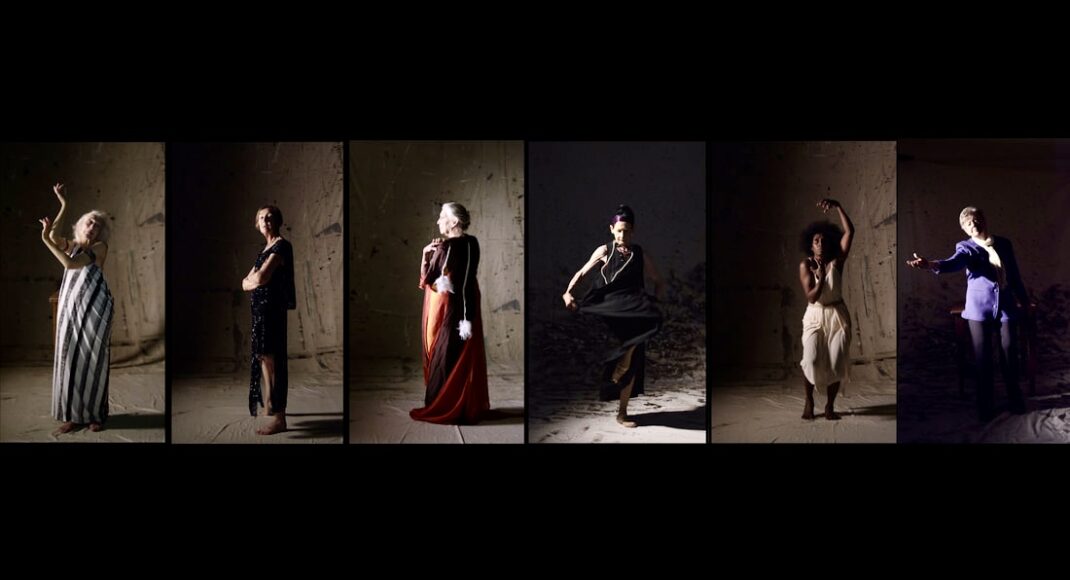
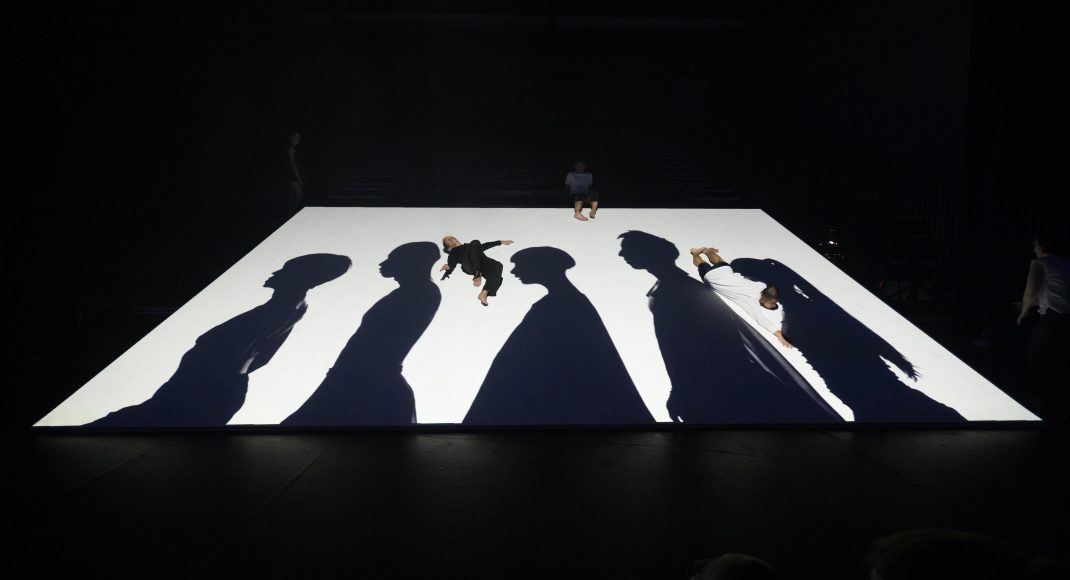
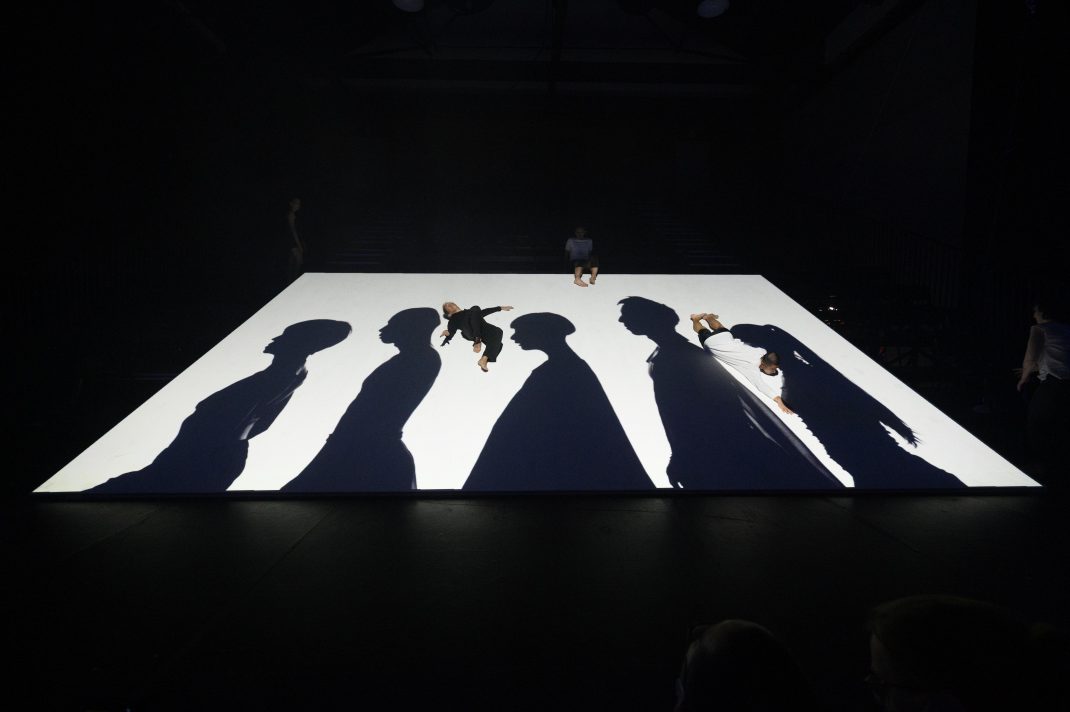
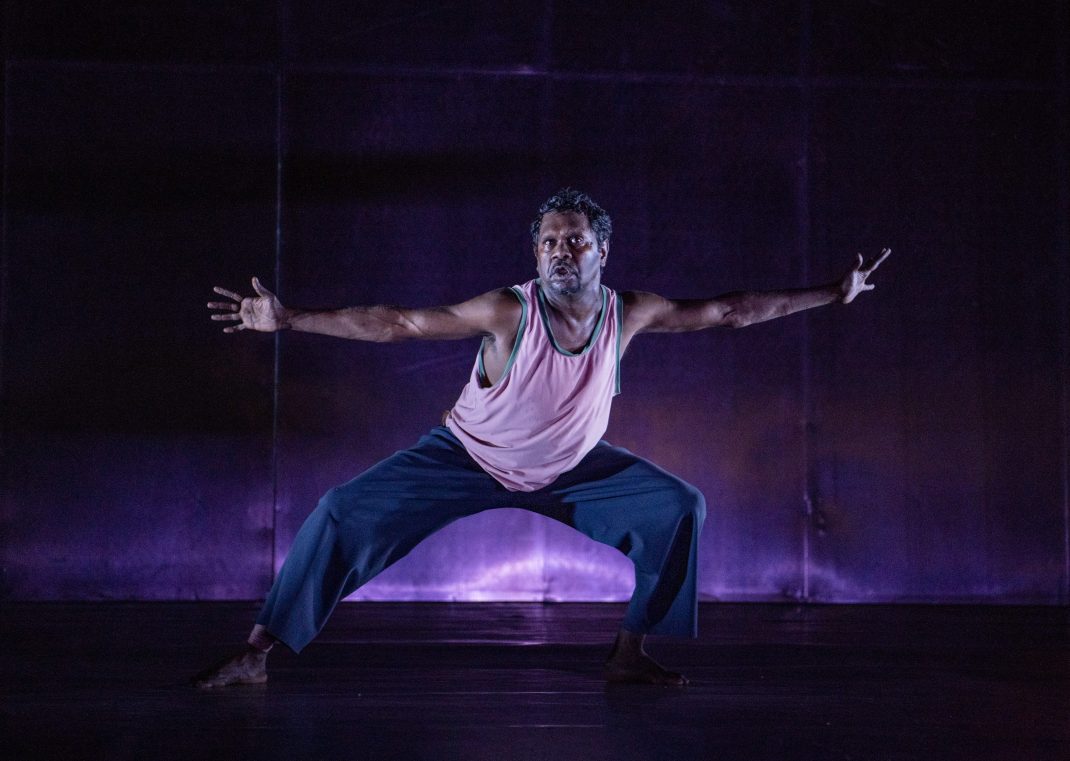
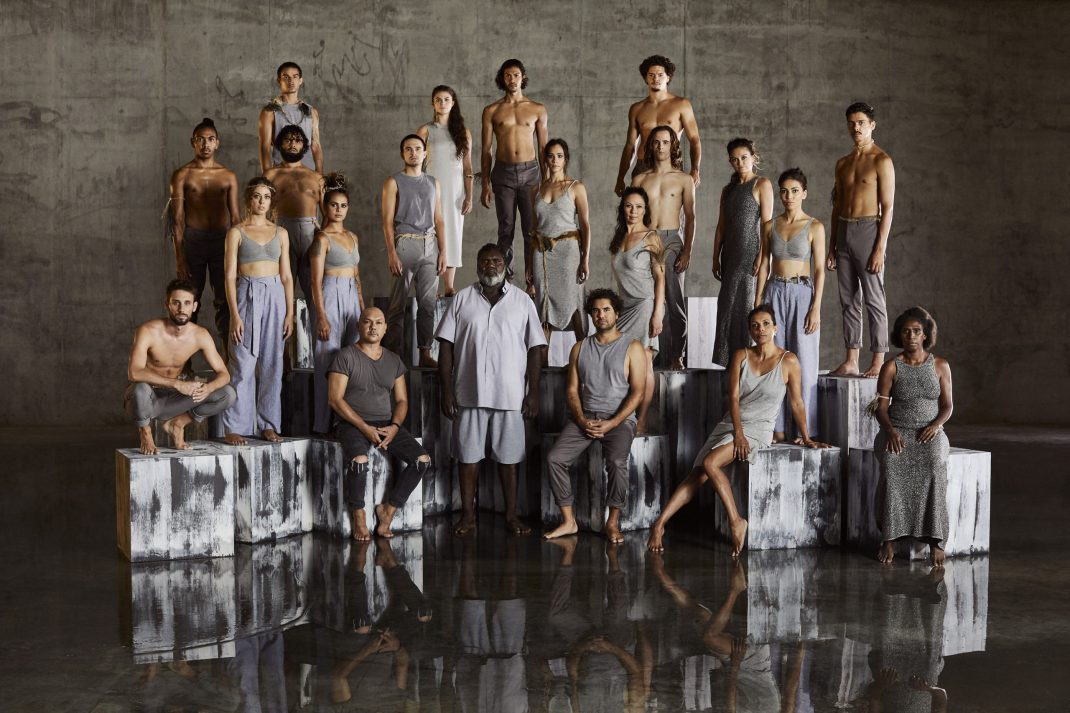
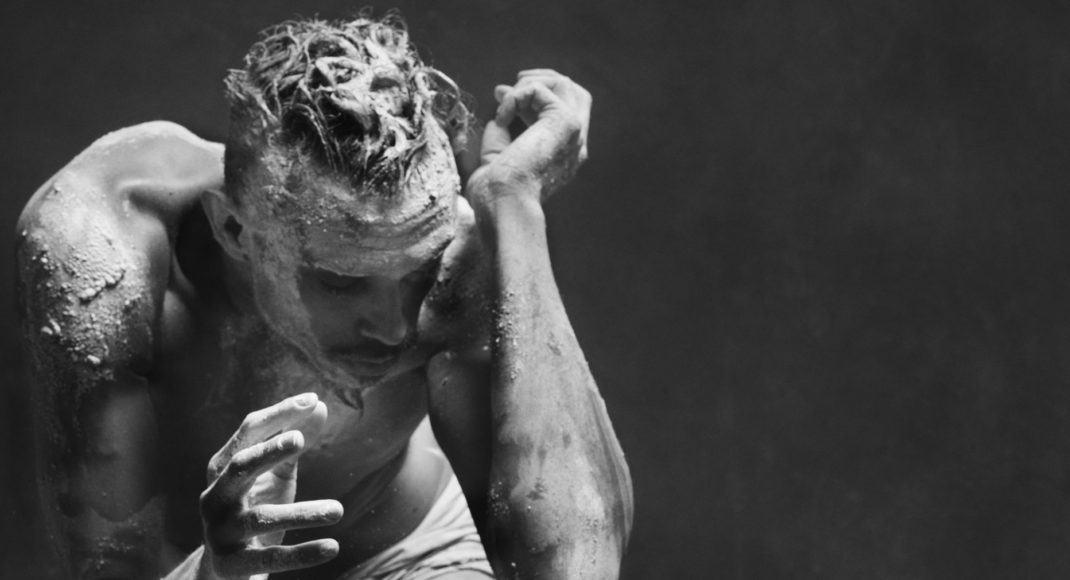
Sue Healey’s latest dance film, On View: Icons, looks at six artists who have contributed remarkably to the growth of dance in Australia. Seen in the featured image, they are (left to right) Eileen Kramer, Nanette Hassall, Elizabeth Cameron Dalman, Lucette Aldous, Elma Kris and Shirley McKechnie. I was privileged to be invited to attend the launch of this latest work from Healey at which the four artists who are still with us (Dalman, Hassall, Kramer and Kris) were present and performed briefly for us. On View has been an ongoing project from Sue Healey and her collaborators for a number of years and in this current iteration some of the footage has been shown publicly before, some has been slightly expanded from previous showings, some is new to this version of On View.
I especially enjoyed the section devoted to Nanette Hassall, which I had not seen previously. Hassall’s exceptional career has included work as a dancer, choreographer and director in Australia, the United States and the United Kingdom. Her achievements have included performing with Merce Cunningham Dance Company, the establishment of the Melbourne-based Danceworks in the 1980s, and the leadership of the dance area of West Australian Academy of Performing Arts (WAAPA) in Perth. Some of the most interesting footage in the Hassall section was filmed by drone cinematographer Ken Butti and showed multiple images of Hassall as a tiny figure twirling and weaving through space.
Nor had I seen the section featuring Elma Kris, whose work I have admired immensely during the period in which she danced with Bangarra Dance Theatre. In On View: Icons we see Kris, a Torres Strait Islander woman, engaging within the landscape and showing us through dance her relationship with earth and water.
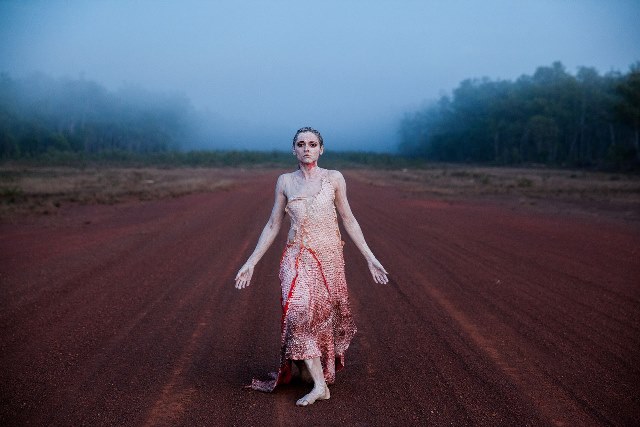
I also loved seeing again Elizabeth Cameron Dalman dancing on the dry lakebed of Weereewa (known to many as Lake George), which is no longer dry but, following recent climate events, is now quite full. The section in which she dances in a white, ‘winged’ costume, reminiscent of that worn on one occasion by dance pioneer Loie Fuller, continues to be quite mesmerising.
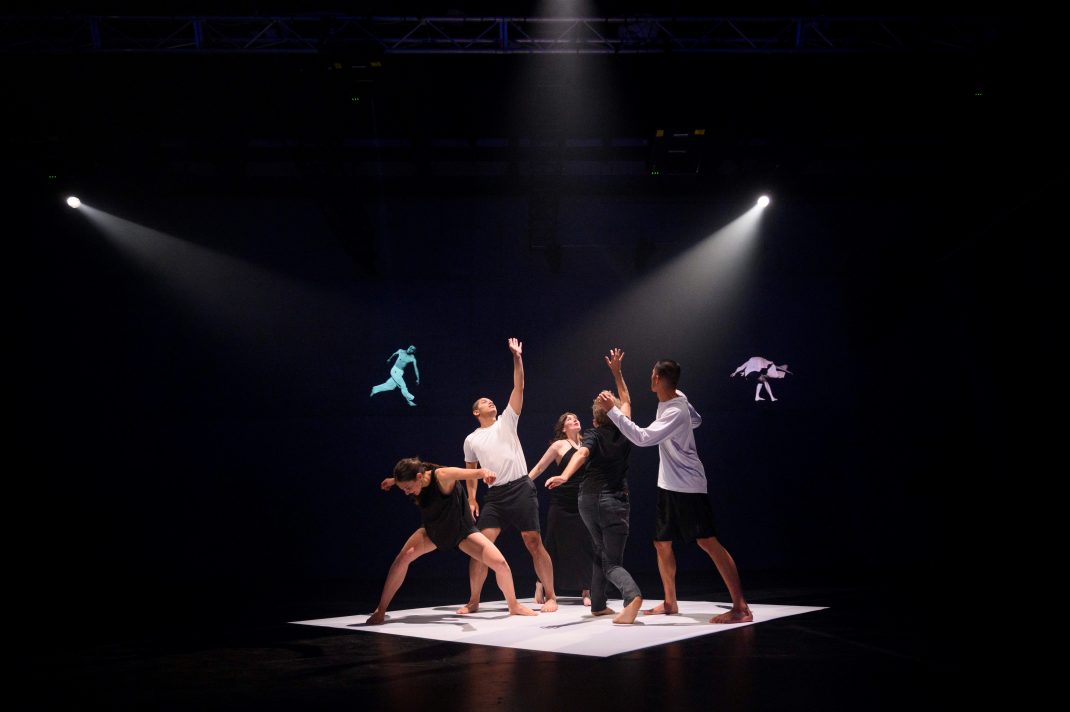
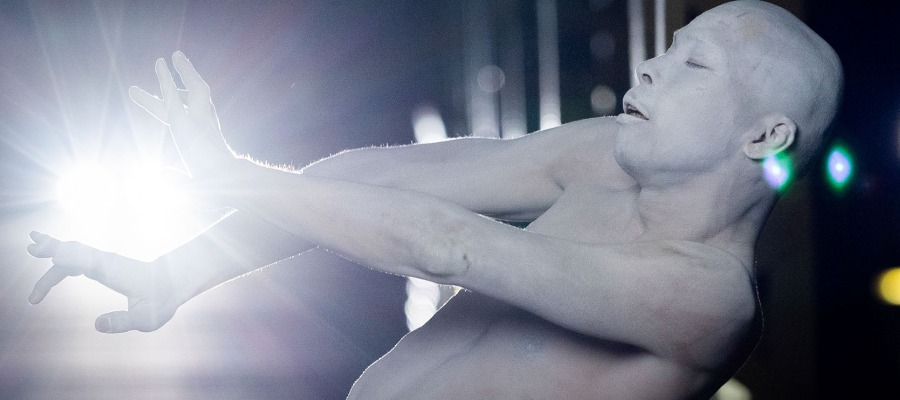
But all six sections were full of beauty and inspired dancing and filming. Healey continues to pay respect to those who have influenced her film making and who, in some cases, have shaped her own career (she danced for example with Hassall’s Danceworks, and her work with Eileen Kramer over the past few years has been extraordinary). Her work with cinematographer Judd Overton and composer Darrin Verhagen has always been a close and exceptional collaborative activity and this version of Icons was no exception.
On View: Icons was a featured event at the 2024 Sydney Festival. Below is a teaser.
Michelle Potter, 20 January 2024
Featured image: Promotional image for On View: Icons.