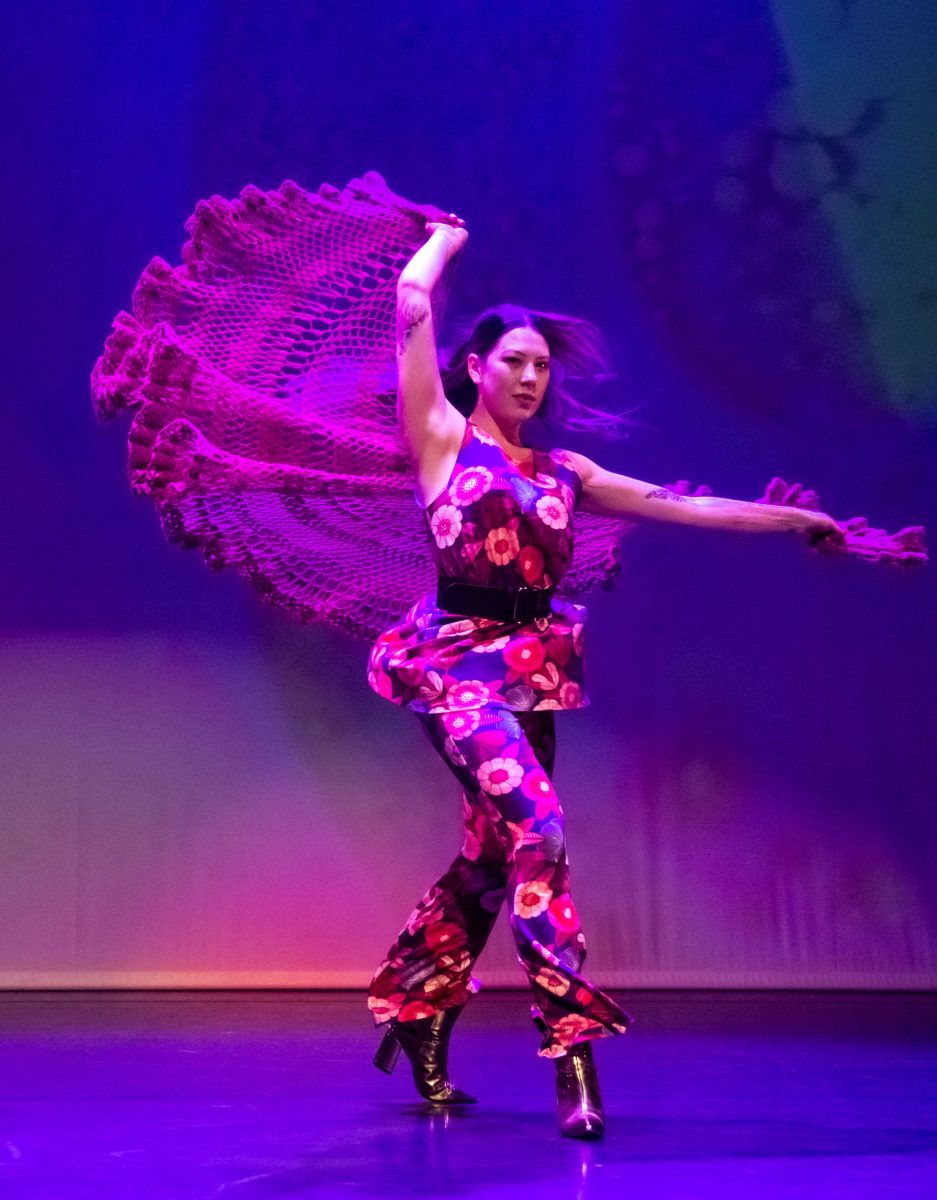
2 – 4 July 2021, Little Theatre, Lower Hutt
reviewed by Jennifer Shennan
For over 30 years Shri Vivek Kinra has been teaching Bharata Natyam in Wellington, at Mudra Dance Academy. There have been hundreds of pupils over the decades, many reaching advanced level and performing the arangetram, two-hour solo recital, that marks their professional debut. Others have arrived more recently in New Zealand and are of Indian, Sri Lankan or Fijian origin. One is of Anglo-Irish descent, proving anyone could be in if prepared to do the work.
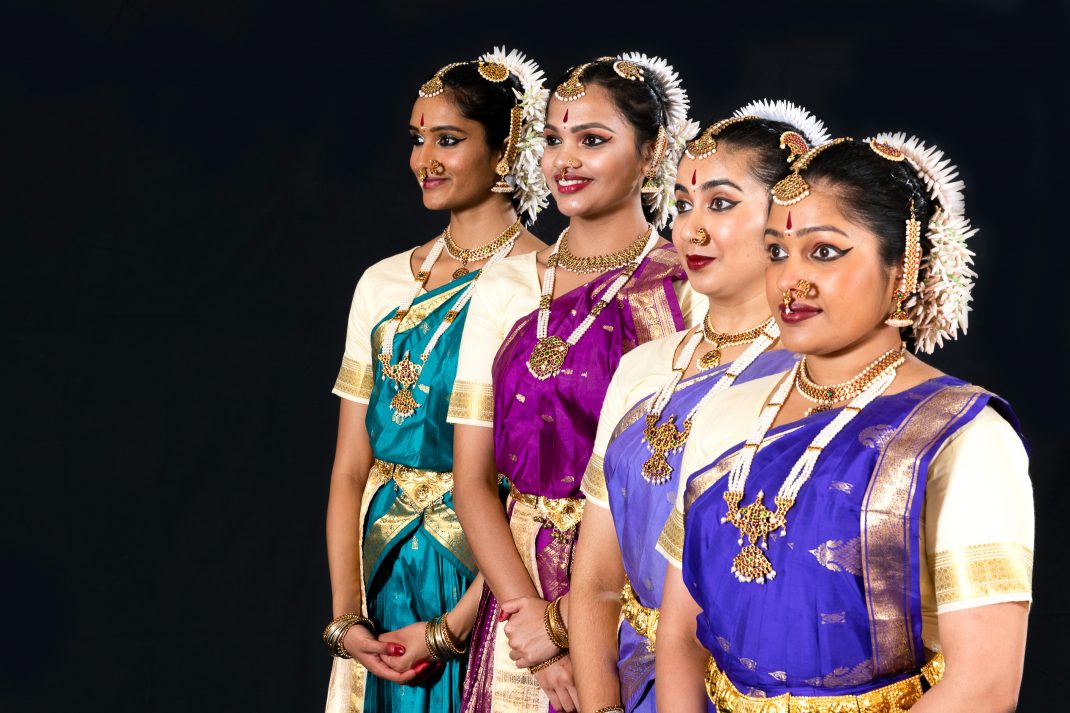
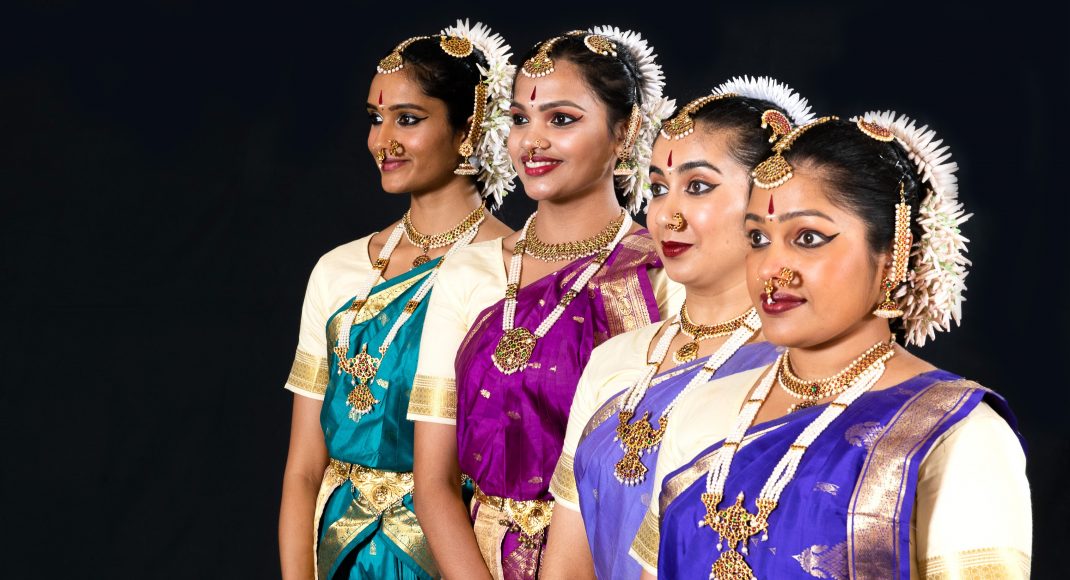
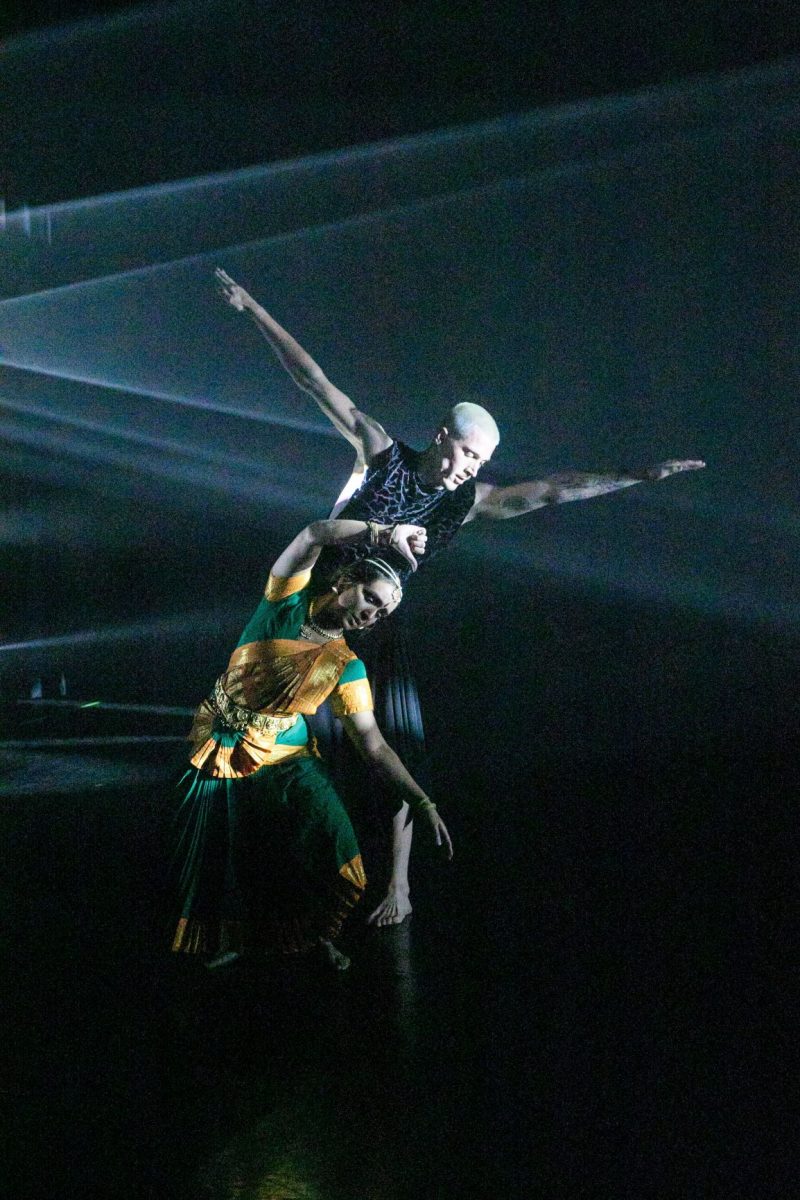
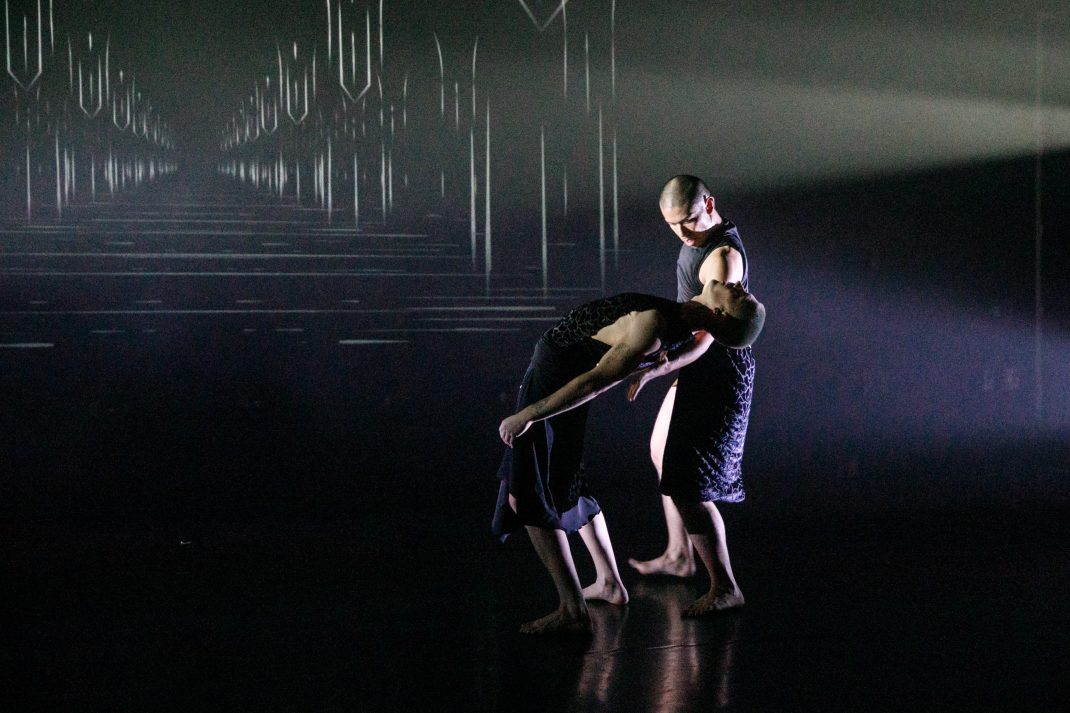
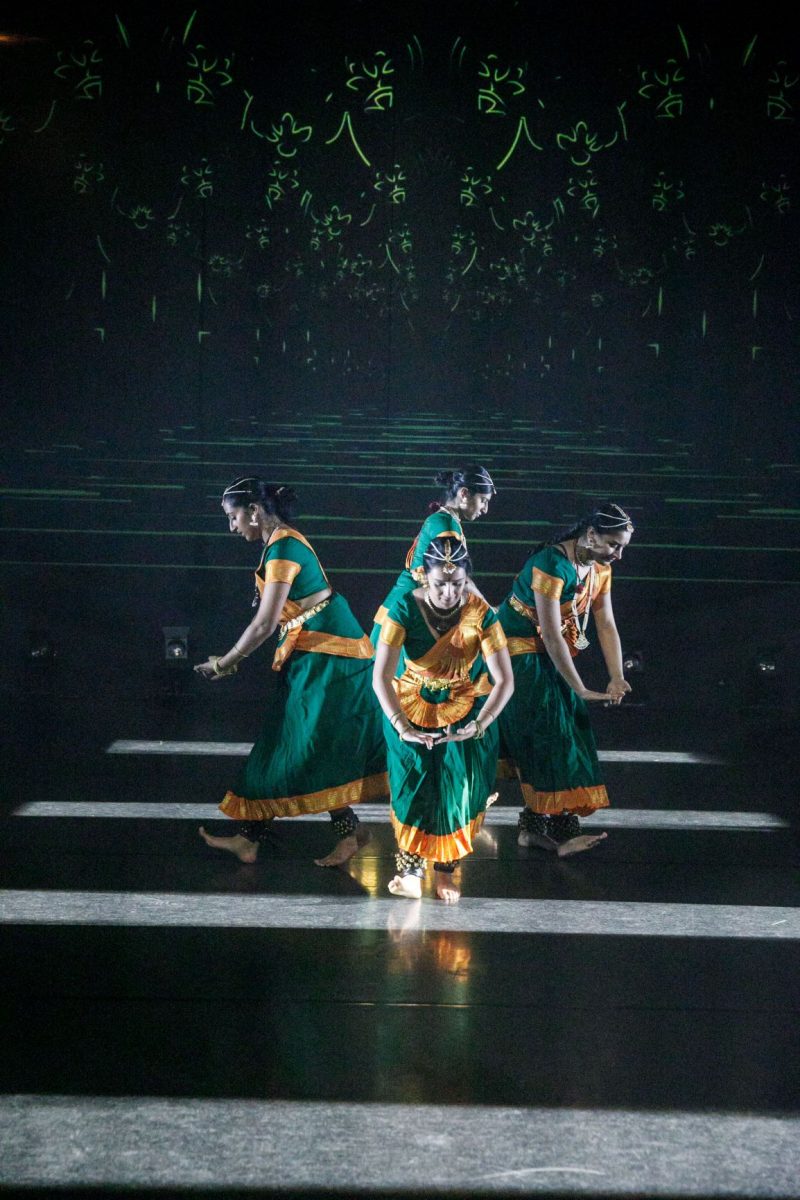
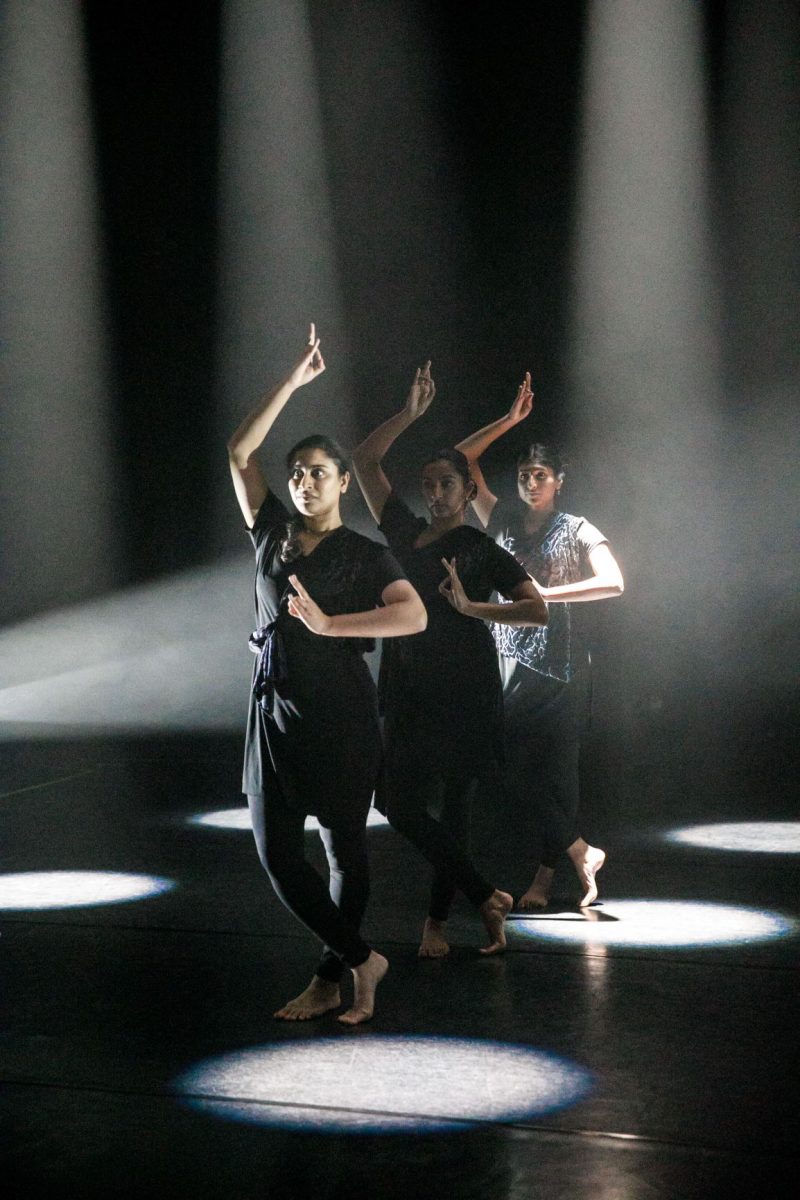
Kinra draws on this pool of talent to form Mudra Dance Company, presenting traditional and new works in seasons that have become a shining beacon in the city’s annual dance program. The technique and expression from each performer is always delivered with the assured musicality that is built in to Bharata Natyam from young pupils’ first class (5 year olds have been known to weep at the door of the Academy since pupils are not accepted until the age of six).
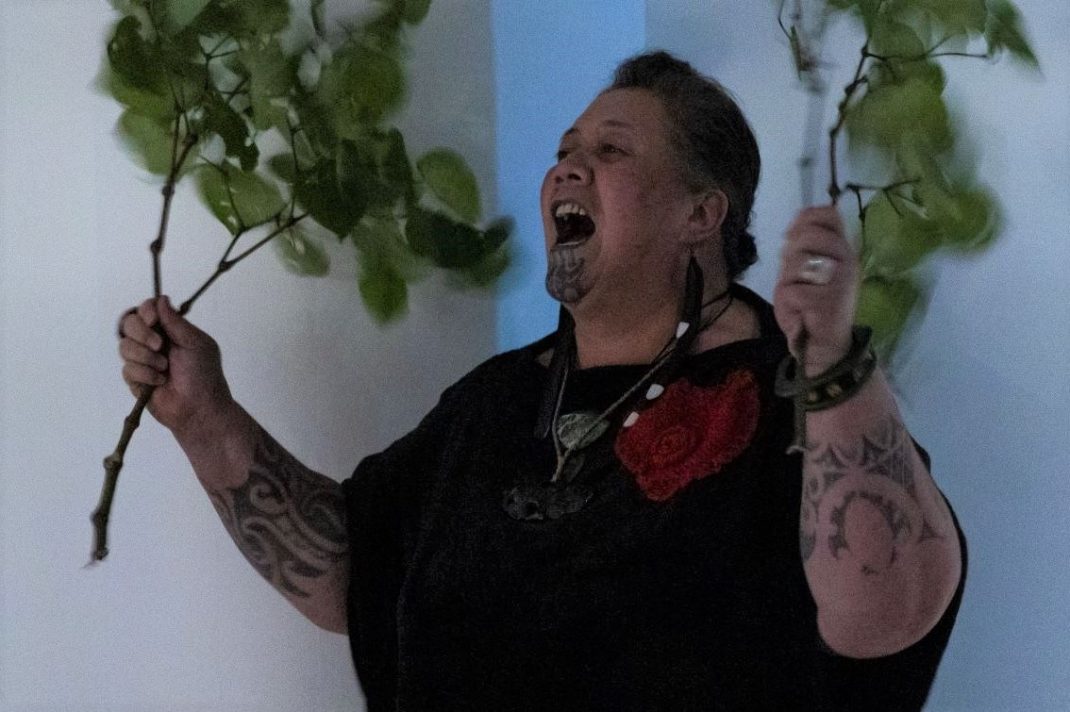
Kinra choreographs and directs these seasons but announced his own retirement from performing in 2015. Fortunately for us he continues to perform mimed cameos of each choreography, by way of narrated introduction to the themes and moods to expect. These little jewels are like dances you can hold in your hand, and are alone worth the time and ticket price. His own training was at Kalakshetra, in Chennai, where he still maintains strong connections, and works with colleagues, Gayatri Lakshmanan chief among them, and the musicians who play the compositions recorded on Kinra’s annual visits to India.
Of the eight items on the program, six are choreographed by Kinra. The main one, Navarasa, which translates as Nine Emotions, lends its name to the whole program.
It is a stunning depiction of the gamut of valour, love, wonder, amusement, disgust, anger, fear, compassion and benevolence as experienced by the Mother Goddess Meenakshi in various encounters with gods, demons, humans and animals both tame and wild. In Tamil sung poetry, it is, as I was expecting, a miniature masterpiece.
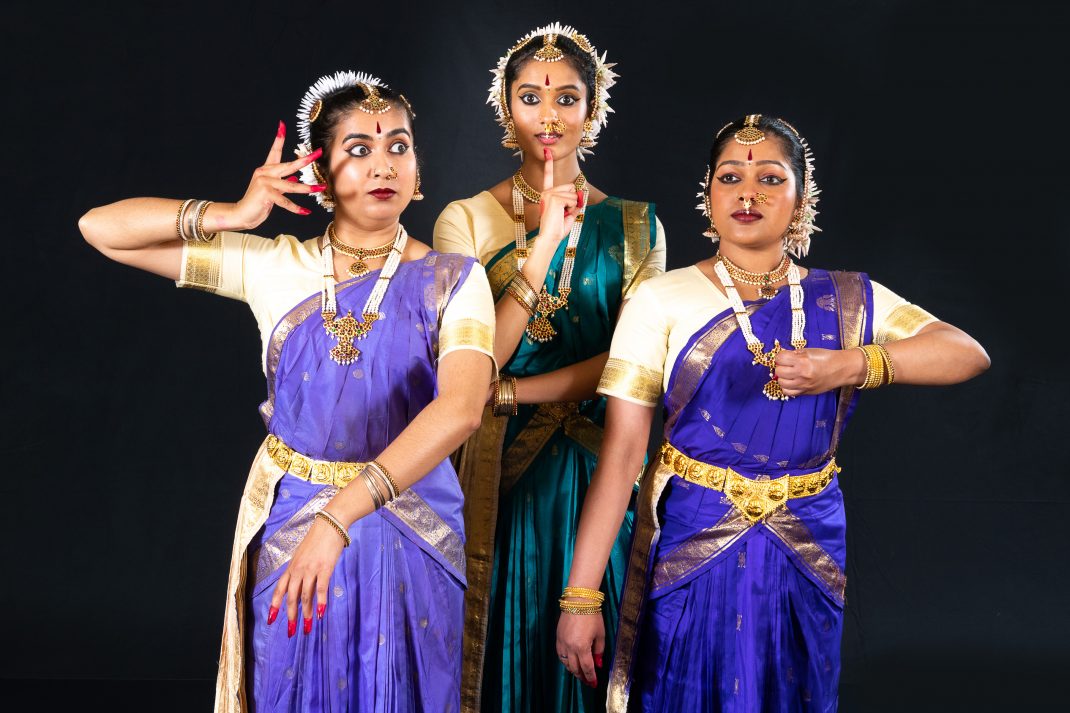

In its mimed prologue, there was a sudden dying of the light. Kinra continued in the dark but knew it would be better if we could see him. A voice cried out for the gods to send light, which will have shaken awake the lighting technician to do as bid, and all was well. Was this part of the choreography all along? A nod to the Covid year that has darkened so many dance stages around the world? Could have been, should have been. You just have to turn the light back on and carry on as before. Vaccines and danced prayers will see us through.
Another item, this time in Sanskrit, is the Shlokas from Shri Krishna Karnamritam. The intoxicating beauty of this god is depicted through musk paste on his forehead, a jewel on his chest, a pearl at the tip of his nose, bracelets, sandalwood paste and a pearl necklace. But wait, there’s more. A herd of cows, a flock of peacocks, dark clouds and strikes of lightning. The piece ends in a dance about dancing—high sophistication this. The Ras Leela is a renowned depiction of ecstasy, usually performed with sticks that percussively mark the beat and interweaving positions of the dancers. Here subtle handclaps were substituted for sticks and it was poignant to hear a swelling response that had a number of the audience gently joining in that handclapping.
I first saw a Ras Leela danced by a large group from the Indian community at the first Pacific Arts Festival in Suva in 1972 (when Kinra was a babe in arms). Performed by 100 dancers out of doors, it was staged by the artists based at the Indian Cultural Centre in Fiji, five musicians and dancers resident in a full-time program for two years at a time, funded by ICCR from India. A short while later Professor Jenny McLeod brought those artists to Victoria University for a memorable intensive workshop at the School of Music. Political events in Fiji followed, the Centre was closed, and the next time I visited Suva it was a sorry sight to see the once vibrant place now empty and derelict with doors and windows creaking on their hinges and banging open in the wind. Life goes on but it’s hard to claim that all of history is progress.
There is a long and interesting history of Indian dance in New Zealand—beginning with Sivaram’s and Louise Lightfoot’s visit in 1950s, Liong Xi in 1960s, Amala Devi in 1970, the Balachandrans, Chandrabhanu, Kanan Deobhakta, two astonishing visits by Kathakali dance theatre, and there are others. Fortunately for audiences who wish to deepen their appreciation of the art, there is a vast literature on the subject. Two leading scholars of the field, Dr Kapila Vatsyayan and Dr Sunhil Kothari, have died recently, but were both aware of Kinra’s work here in New Zealand, in the world map of dance.
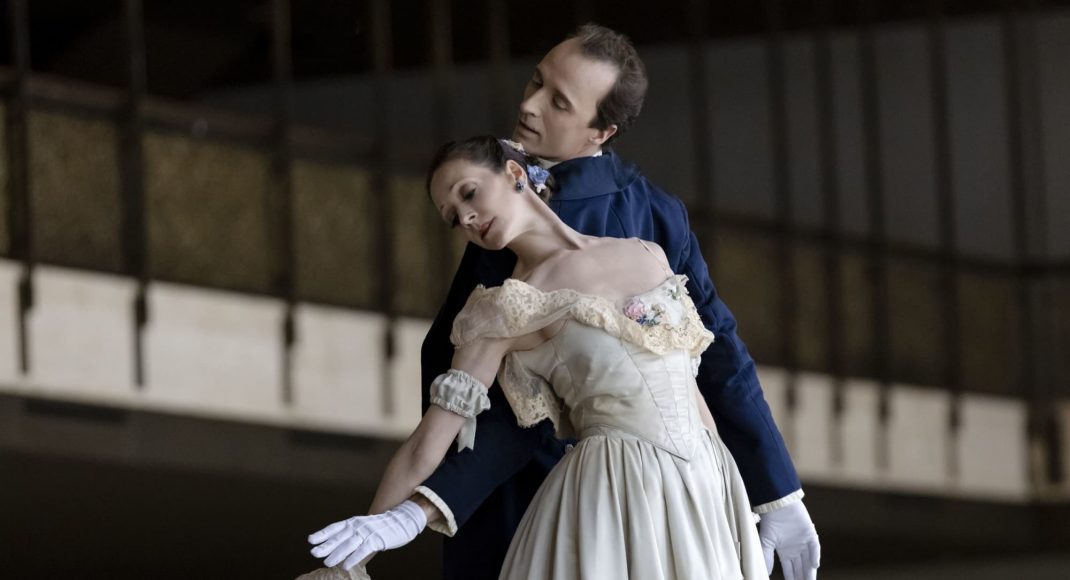
There was an exuberant cadence to the performance in the final Thillana, choreographed by the late Rukmini Devi, founder of Kalakshetra. (She too once visited New Zealand, as guest of the Theosophical Society). Mudra’s line-up of radiantly costumed and bejewelled dancers was a joy to the capacity audience. It is not to demote any of their previous memorable seasons to mark Navarasa as their strongest choreography yet.
Jennifer Shennan, 03 July 2021
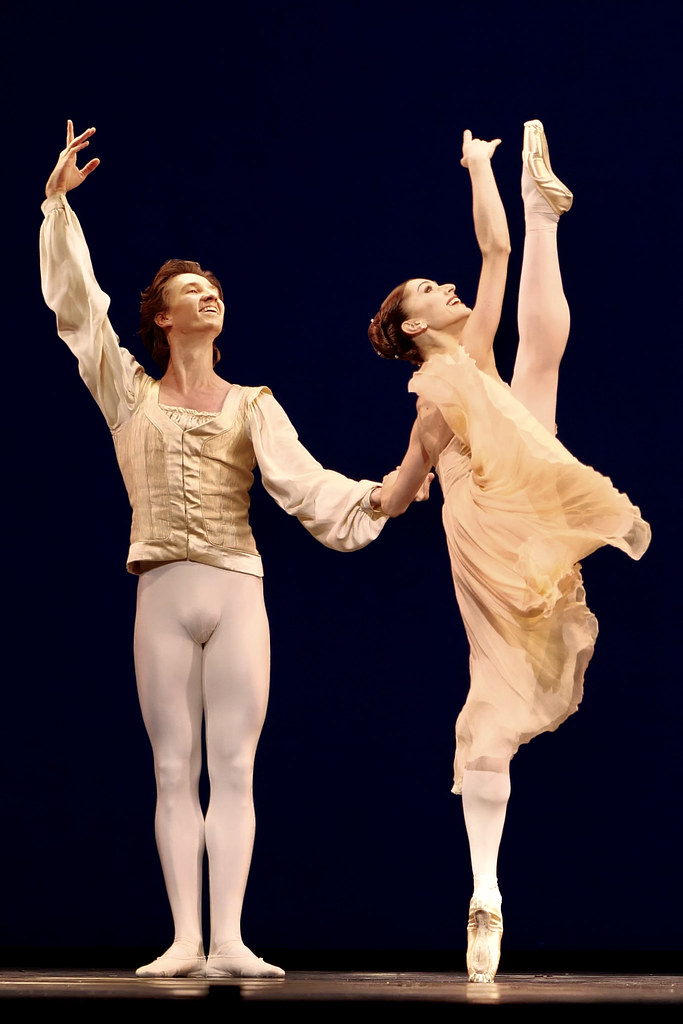
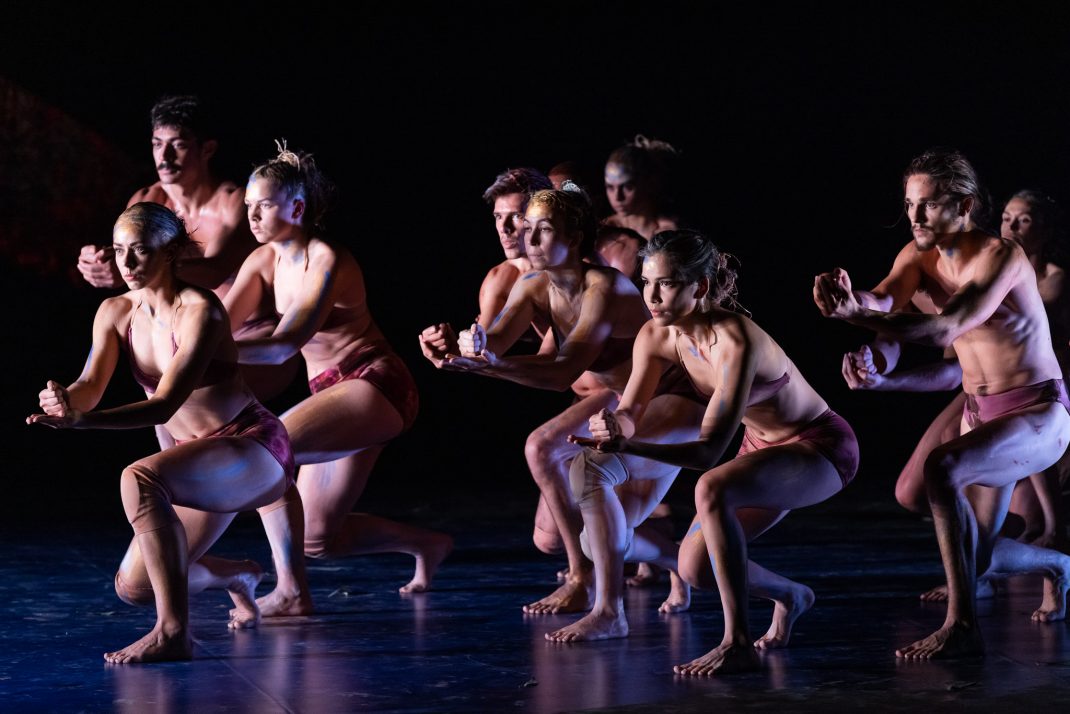
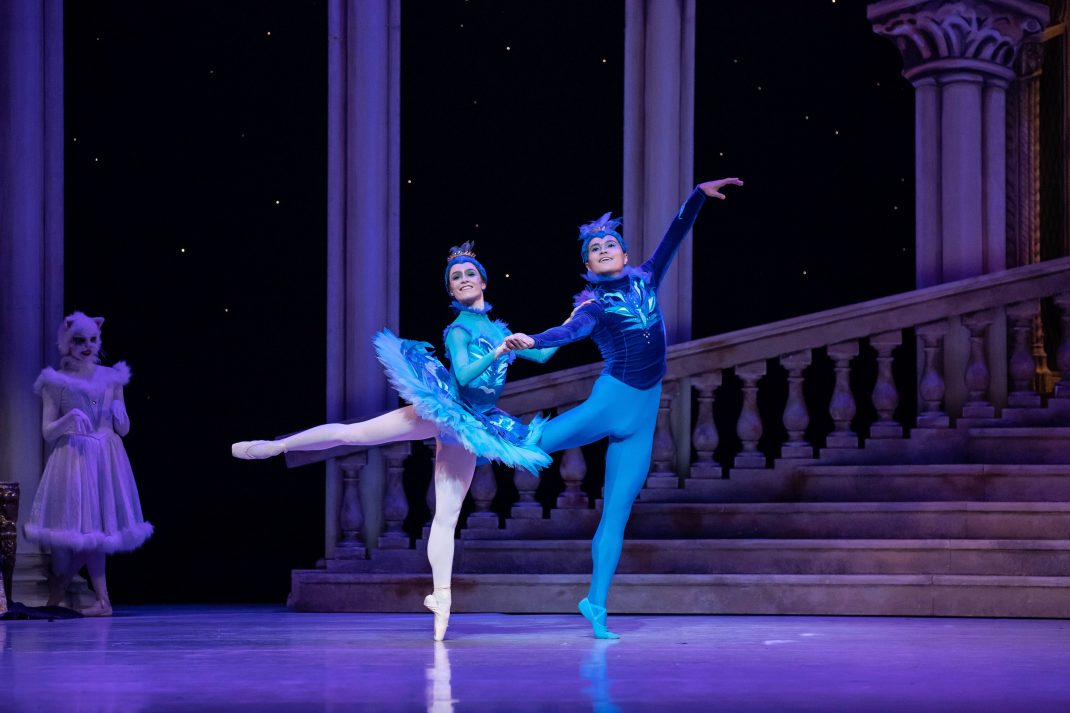
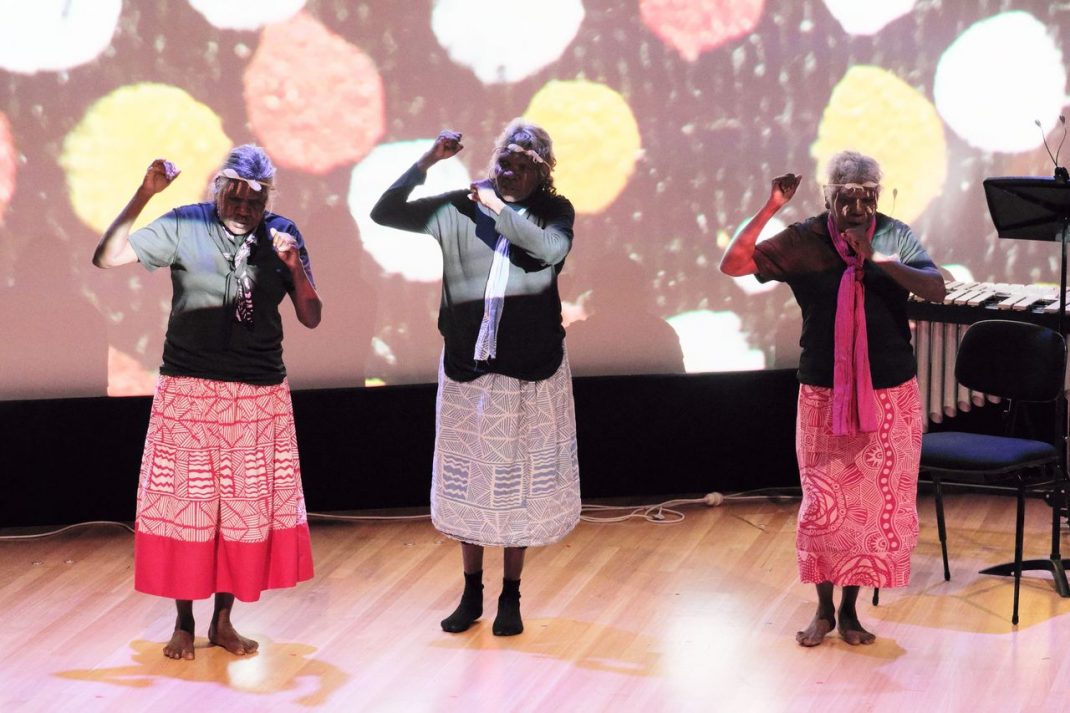
Featured image: Senior dancers of the Mudra Dance Company, 2021. Photo: © Gerry Keating