- Australia Council dance news
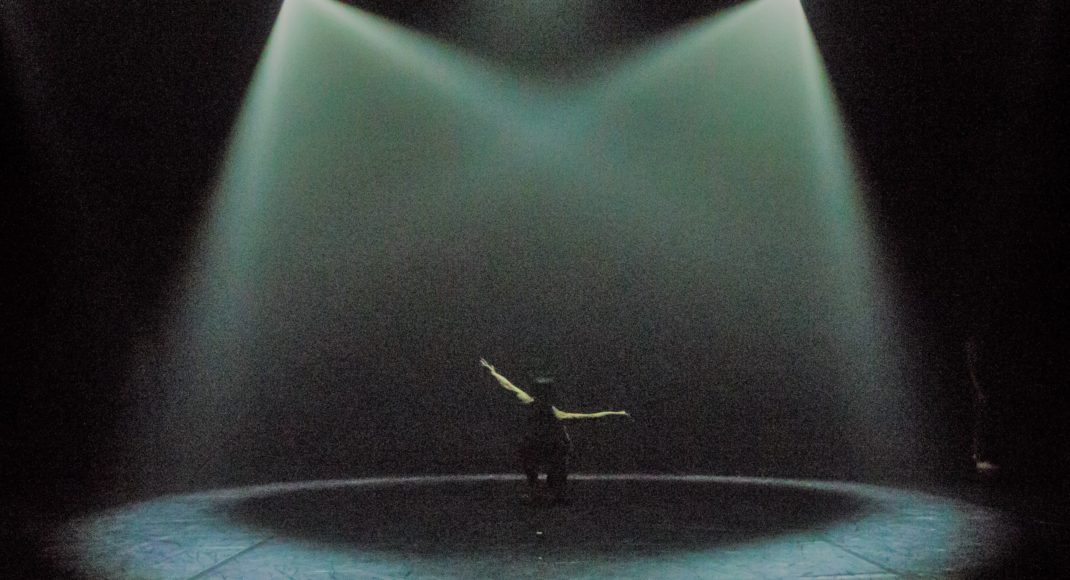
During March the Australia Council announced the results of grant awards for international residences. I was especially interested to note that West Australian choreographer, Rachel Arianne Ogle, is the recipient of a residency at the Cité internationale des arts in Paris. I admired her work Of Dust at Sydney Dance Company’s 2016 New Breed season. In Paris she will work on creating a series of short solo works that will be the foundation for a new full-length work. I look forward to seeing the outcome of this residency.
Other dance awardees include Anna Seymour, born profoundly deaf, who will spend time in New York at the Omni International Arts Centre; Matt Shilcock from Adelaide who will work with Helsinki dance companies; and Melbourne-based Natalie Abbott who will also work in Helsinki.
- The search for identity. Australian dance in the 1950s
At the recent BOLD Festival in Canberra I delivered a paper entitled The search for identity. Australian dance in the 1950s. Among the several works I looked at was Terra Australis, made for the Borovansky Ballet in 1946, which I considered as a forerunner to the many works on Australian themes that were choreographed in the 1950s. Looking at Terra Australis now, it stands as quite a remarkable production for its time. I was able to play, as part of my presentation, an excerpt from a radio interview with librettist Tom Rothfield, and some footage from both the 1946 production and the restaging in 1947 when the work had new designs.

What especially stood out in the Rothfield interview was the fact that he made it very clear that he and Borovansky had focused on the the fate of the Indigenous population at the time of white settlement. In fact, he spoke strongly of the fact that he and Edouard Borovansky, who was choreographer of the work, hoped to provoke the audience into understanding what he referred to as the ‘true story’ of the arrival of Europeans. Very provocative for the 1940s.
In my research for that paper I also uncovered some interesting material relating to Camille Gheysens, a Belgian-born composer who made his home in Australia and who composed several pieces of music for Gertrud Bodenwieser, including her 1954 work Aboriginal Spear Dance. Gheysens’ patronage of Bodenwieser was significant, although perhaps not without its problems. Bodenwieser dancer, Anita Ardell, in her 2001 oral history interview for the National Library, remarked:
‘I don’t think that Madame really loved his music. Werner Baer certainly didn’t, and he was the musical director of the ABC at the time. But Madame was a very practical person. If this man were going to provide costumes and venues for her choreography, then so be it.’

The research period was certainly a thought-provoking time and I hope eventually to be able to post the paper on this site.
- Trisha Brown (1936–2017)
I was saddened to receive the news of the death of American choreographer Trisha Brown, a most remarkable pioneer of postmodern dance. Alastair Macaulay’s obituary for The New York Times is at this link.
My opinion of Brown’s works comes from seeing her company not in New York or anywhere in America, but from performances I have seen in London and Paris. In particular I still remember with huge pleasure a set of dances the company performed at London’s Tate Modern several years ago—my review is at this link. I also had the pleasure of seeing Glacial Decoy danced by Paris Opera Ballet and, just recently, I was reminded of this particular work when some brief footage from it, along with Rauschenberg’s photographs that slid across the back screen throughout the work, were shown in the Tate’s recent Robert Rauschenberg retrospective. Vale Trisha Brown. The small amount of her work that I saw gave me much pleasure.

Michelle Potter, 31 March 2017
Featured image: Scene from Rachel Arianne Ogle’s Of Dust. Sydney Dance Company’s New Breed season, 2016. Photo: © Pedro Greig