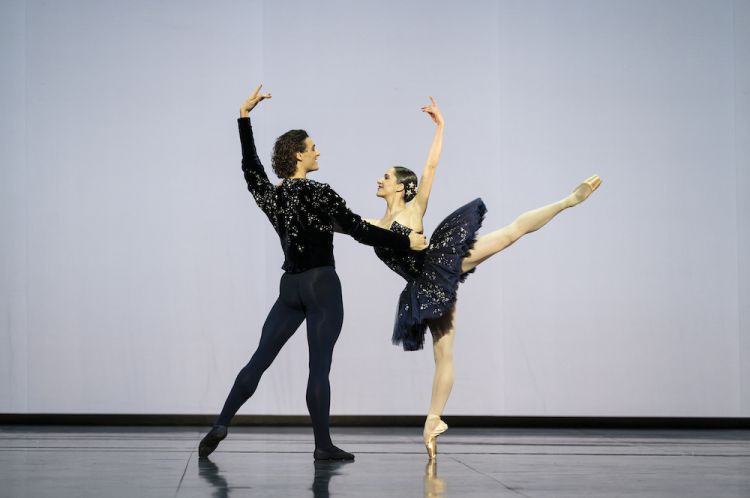
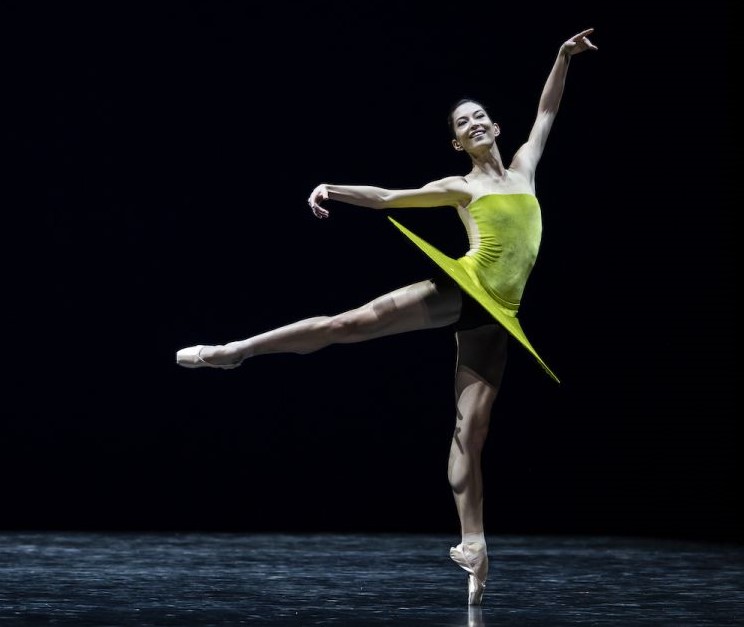
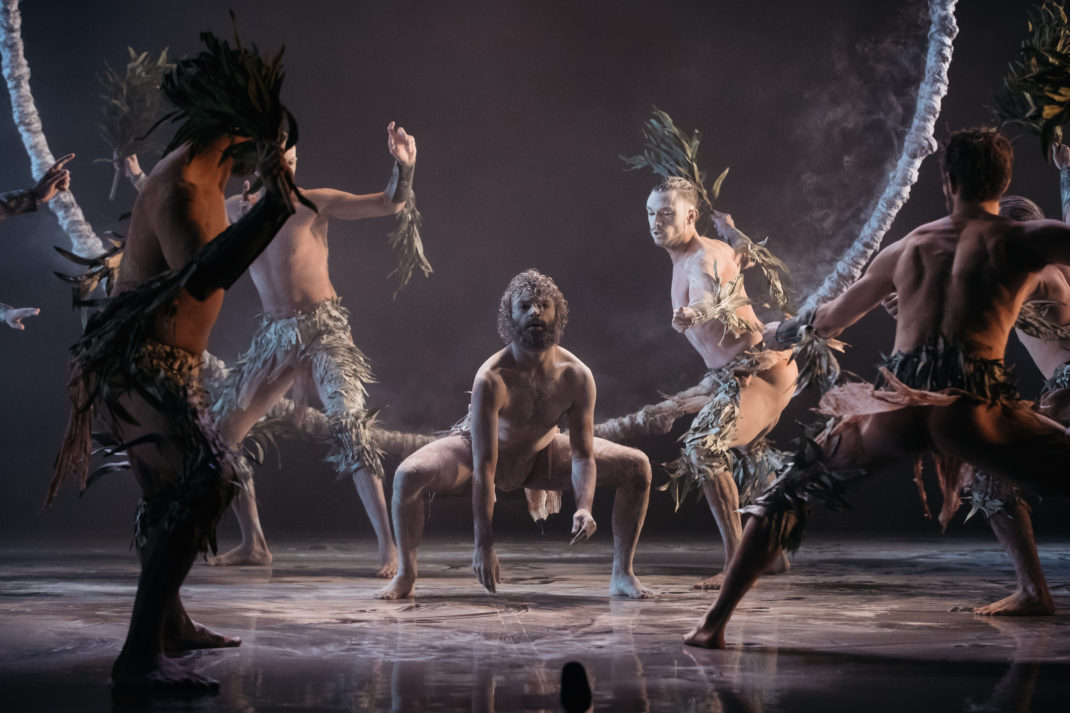17 April 2021 (matinee). Joan Sutherland Theatre, Sydney Opera House
The first thing to say about this first Sydney program for 2021 from the Australian Ballet is that the dancers look fabulous. They are in terrific form in a technical sense and seem absolutely to relish being back onstage after a grim 2020. Watching them perform was a real thrill.
The program was certainly an interesting one and at the end it became clear what the ‘dialect’ of the title was (or was not) all about. The language of each of the three works, Serenade and The Four Temperaments, both by George Balanchine, and Watermark by Pam Tanowitz, was very much about the vocabulary of ballet (contemporary and otherwise) and the way that vocabulary can be arranged onstage. I’m not sure, however, that this is specifically a New York dialect, except that the two choreographers are or were New Yorkers. If we think of dialect as being a form of language specific to a particular region, it seems to me that what we saw was a choreographic dialect from people who happen to be New Yorkers. I guess I didn’t much like the title of the program. But I did like the dancing and in some cases the choreography.
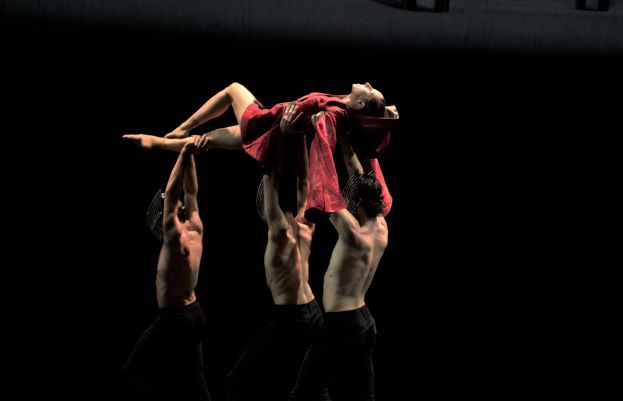
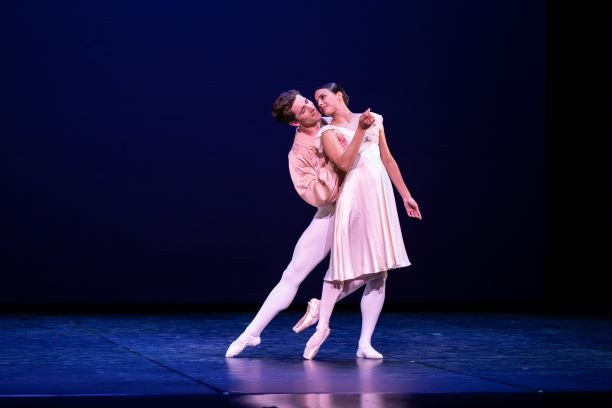
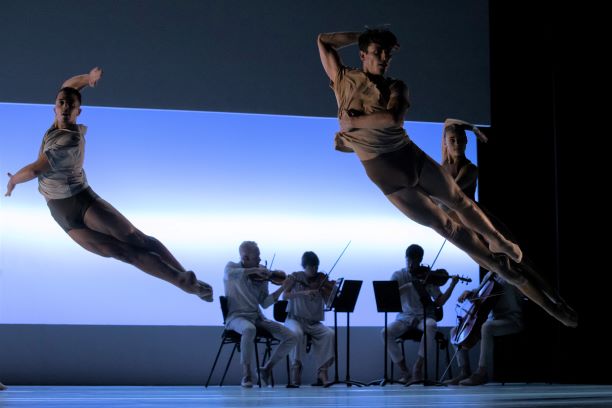
Serenade has always been a beautiful way to start a program. Although Balanchine liked to say his ballets didn’t usually have a story behind them, I love those moments when there is a backstory there. In Serenade there is the girl who arrives late, for example, and also the mystery ending when two dancers embrace and one is then lifted high and carried into the distance. What has happened? What will happen? Then there’s the opening scene. It always generates a frisson of delight, even though it is expected.

Throughout the work, Balanchine’s masterful groupings and use of the stage space, and his particular take on the classical vocabulary, are clearly on view. A work to watch over and over.
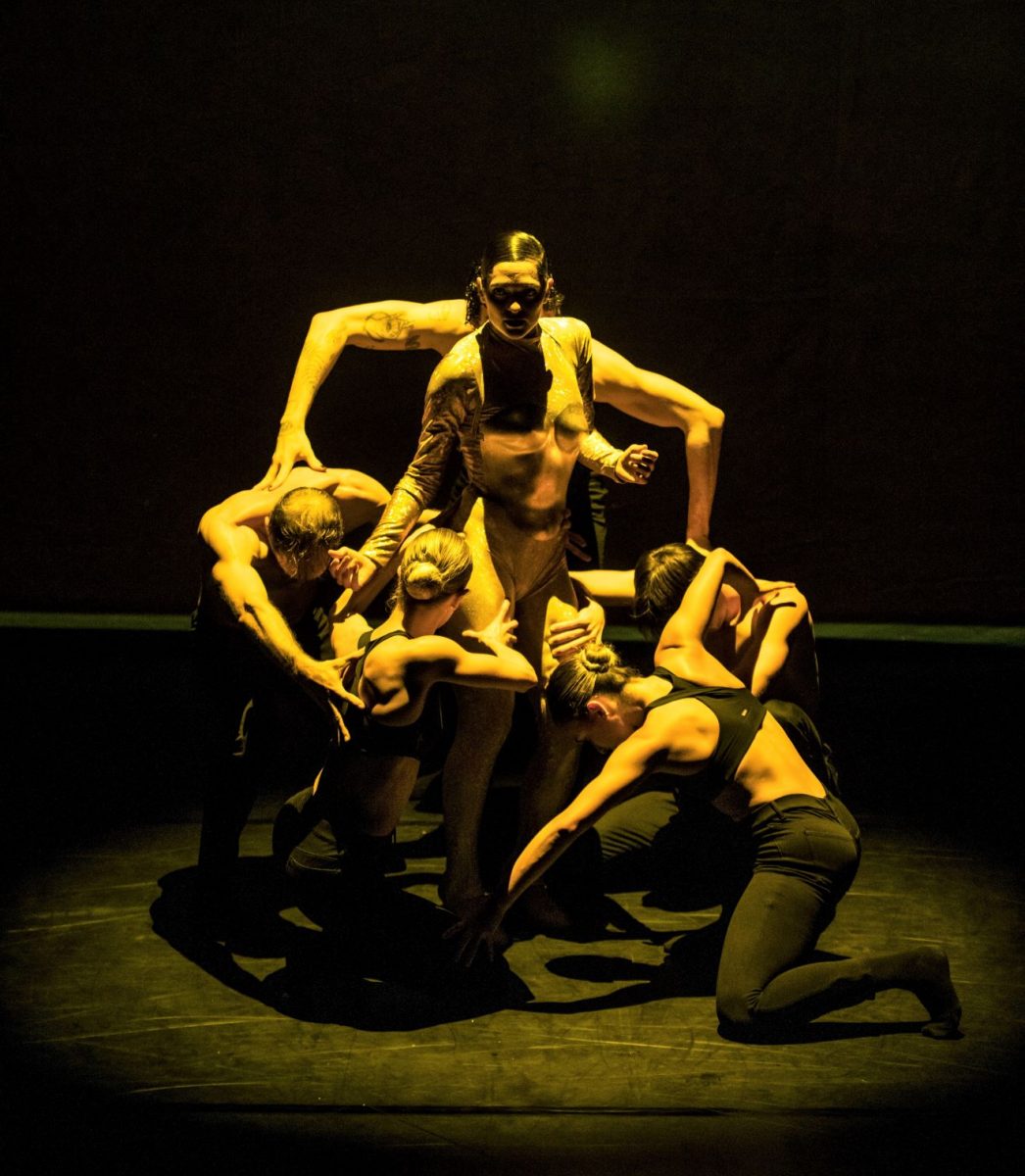
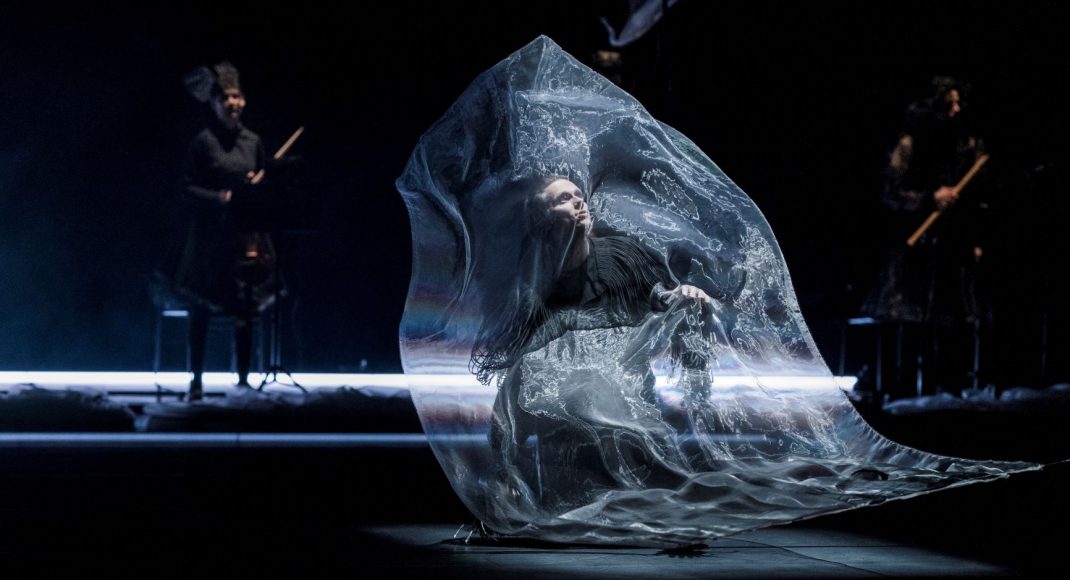
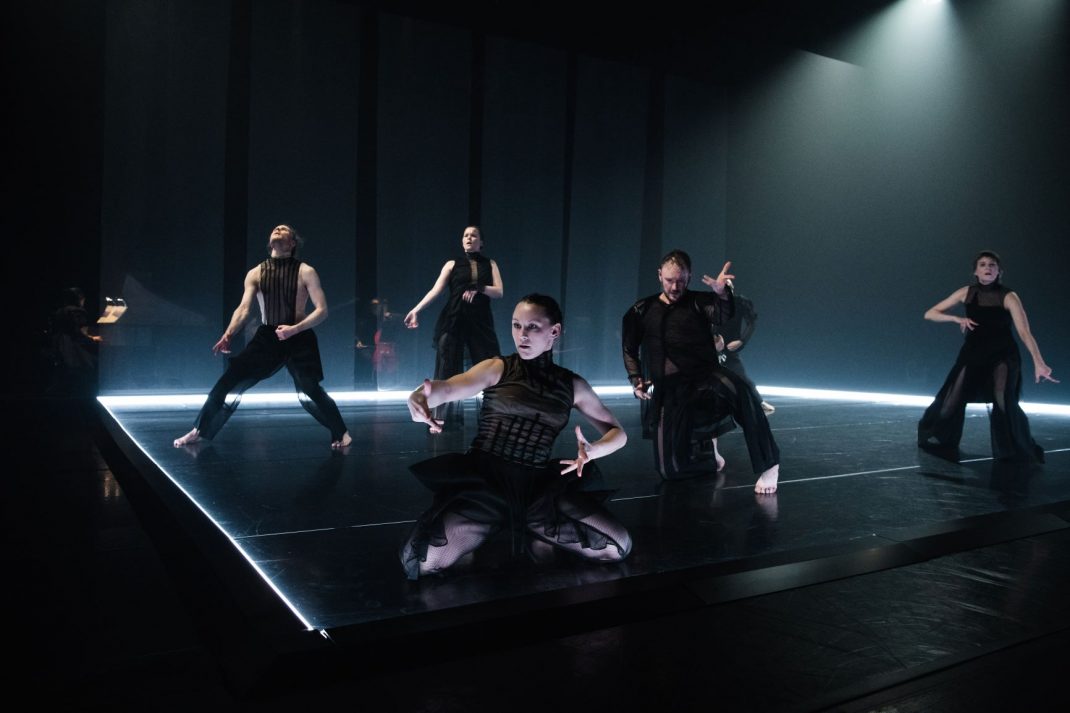
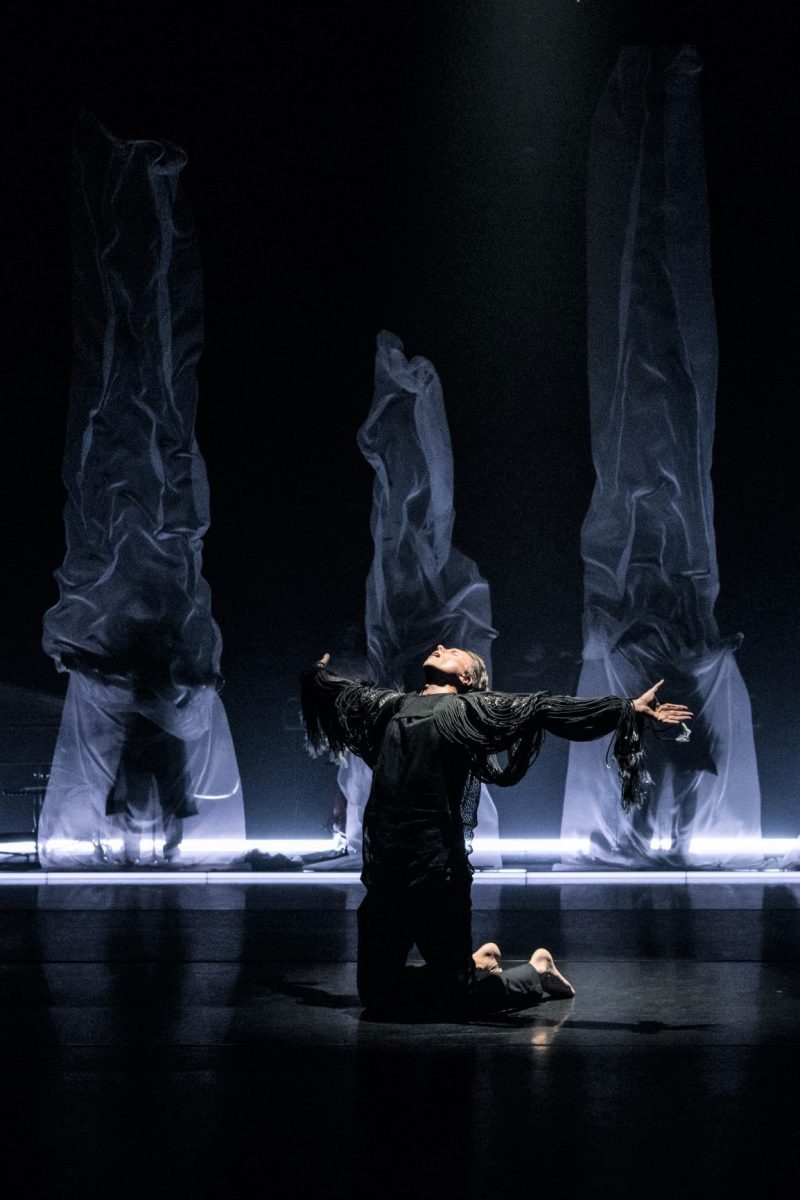
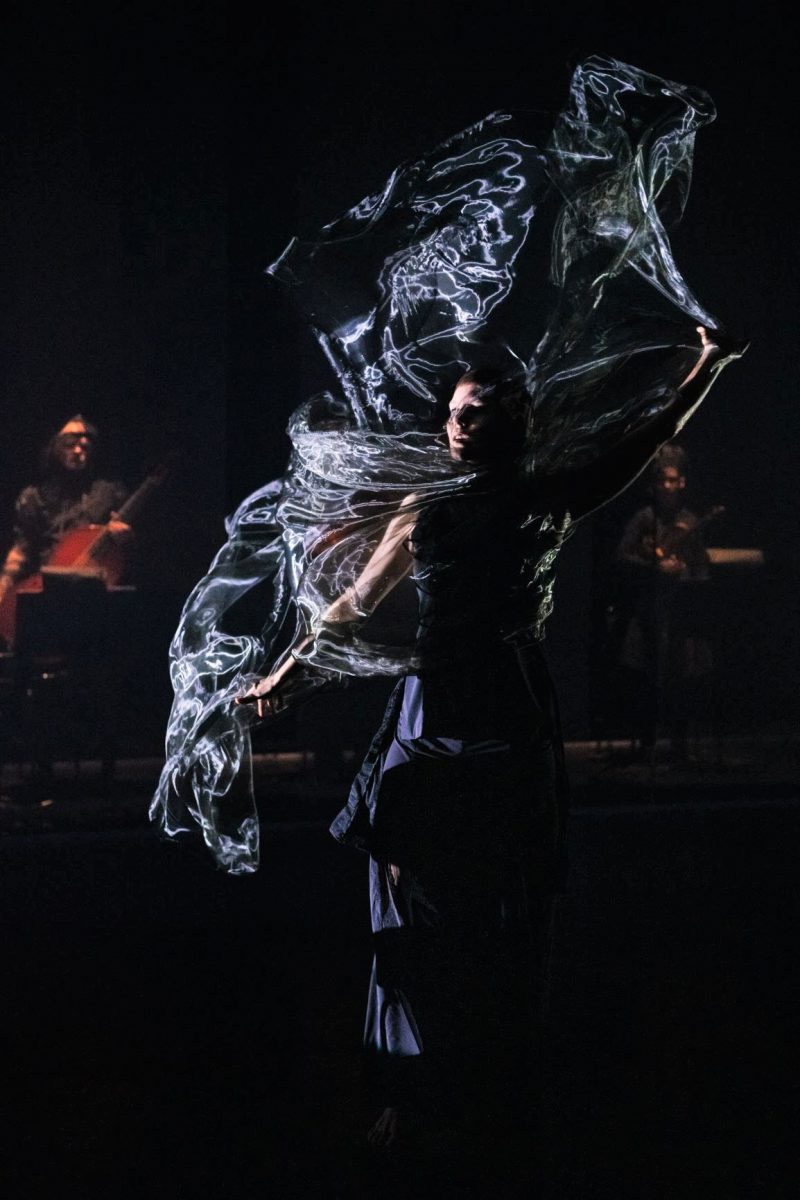
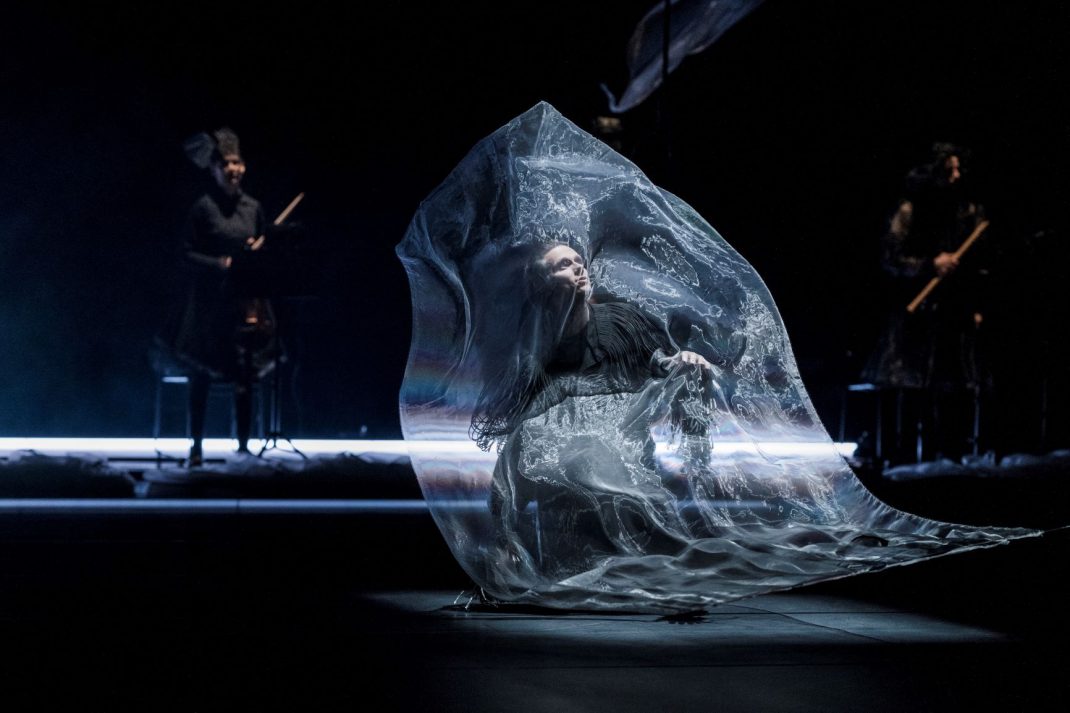
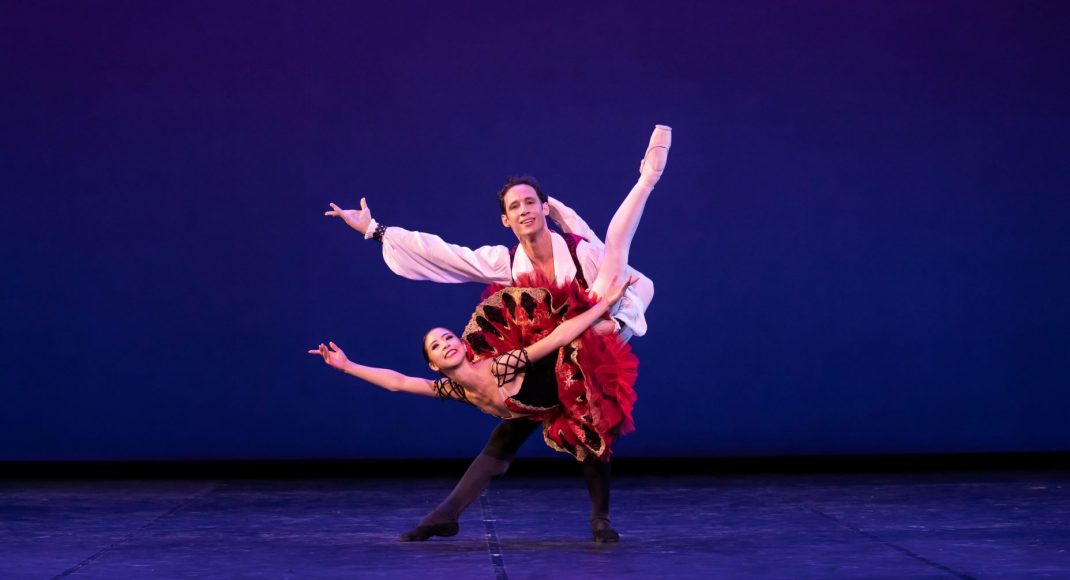
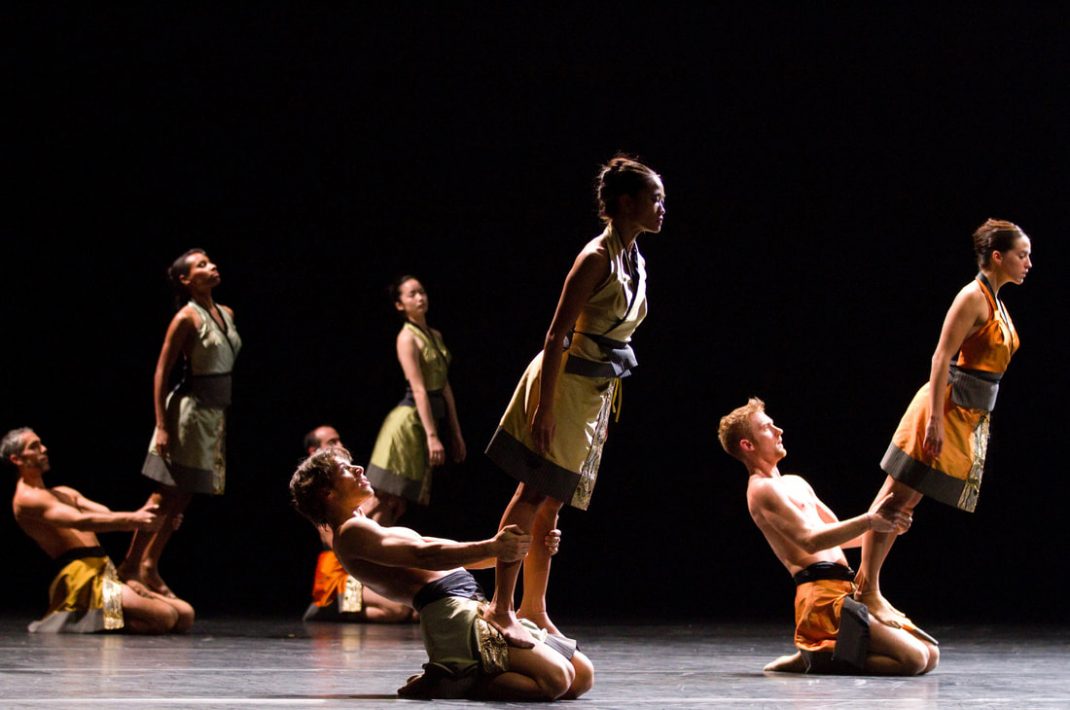
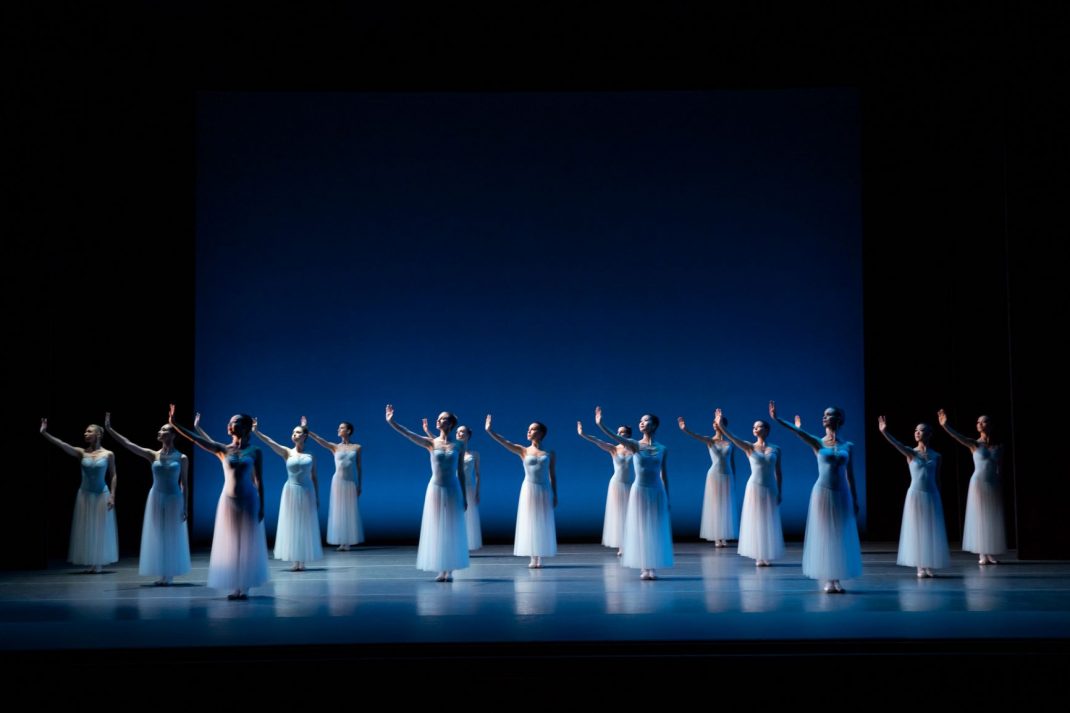
Second on the program was a new work from Pam Tanowitz, Watermark. I have to ignore that title because it seemed meaningless in relation to the work. Tanowitz’s vocabulary was quirky in parts, with its beats done with feet as if in first position, its jerky arm and hand gestures and its frequent use of drooping bodies. Tanowitz counts former Cunningham dancer Viola Farber as one of her mentors and where the vocabulary was not so eccentric it reminded me a lot of the Cunningham style with its off centre movements and its jetés that never tried to look as though they were like splits in the air.
I also wondered why a line of dancers, midway through the piece, needed to come onstage from the auditorium? And I couldn’t enjoy the ending when the stage space was virtually empty and all the dancers were lined up along the wings. It just seemed like trying too hard to be different. This is the second work by Tanowitz that I have seen and I can’t say I have really enjoyed either of them.
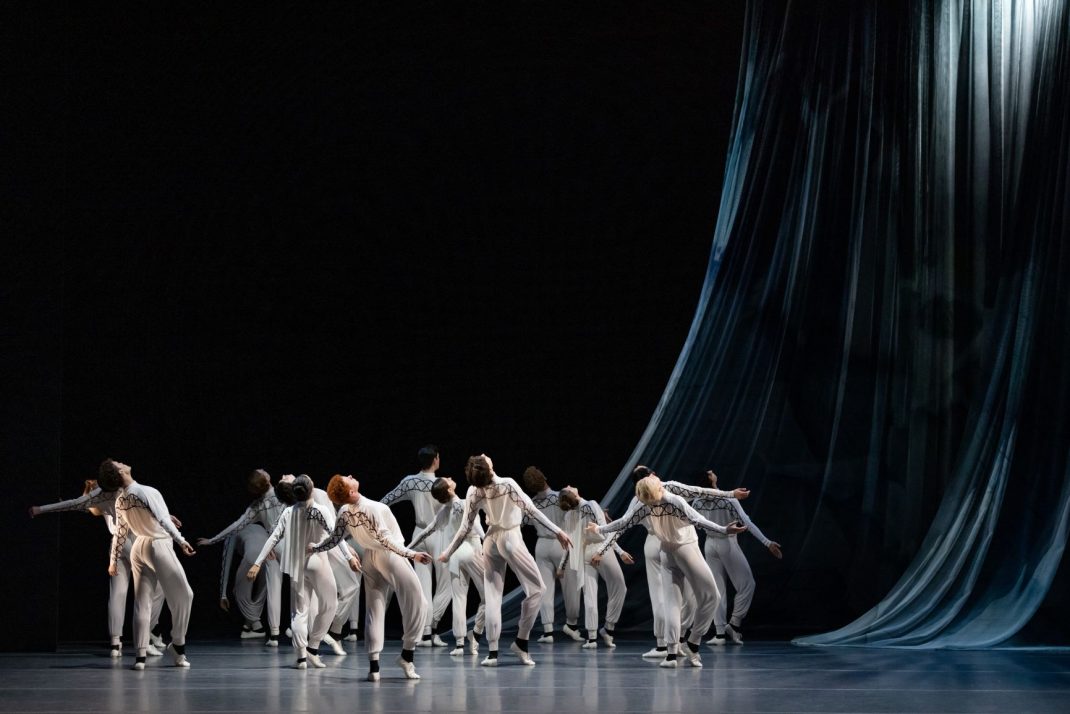

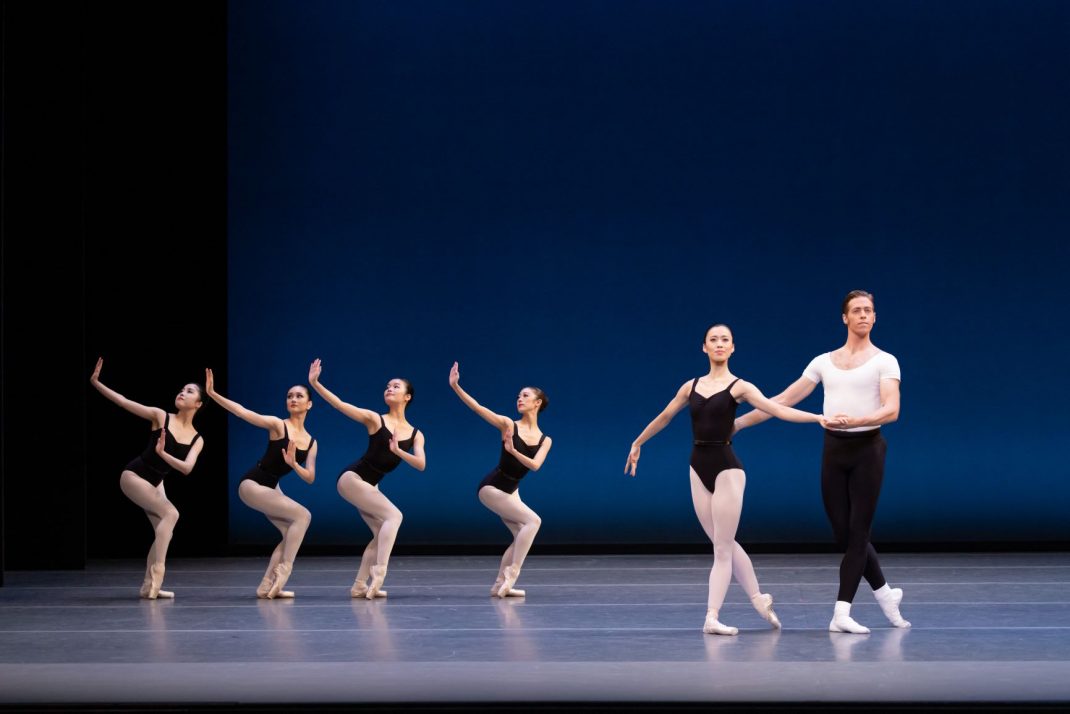
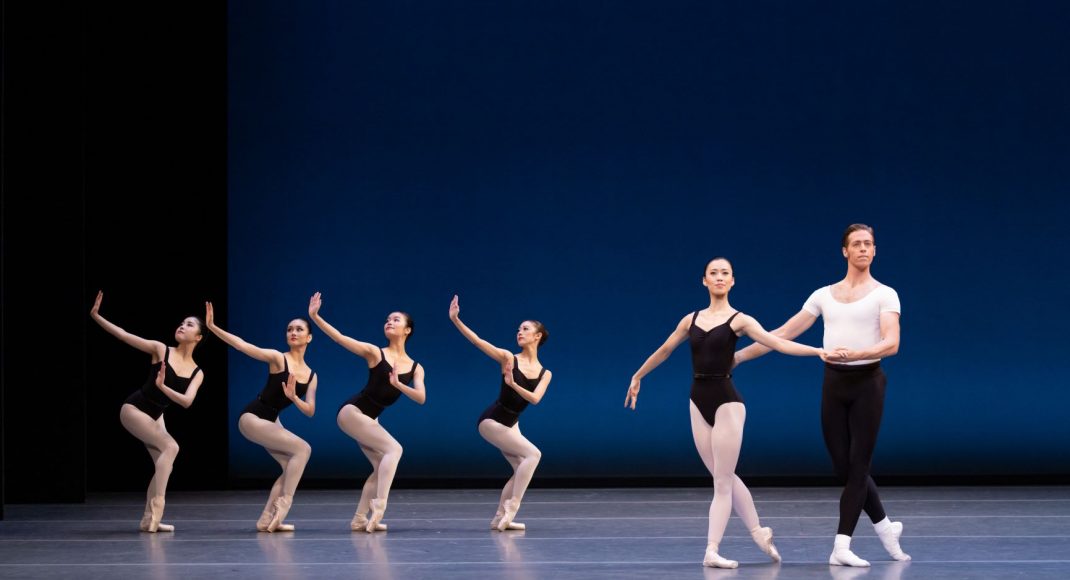
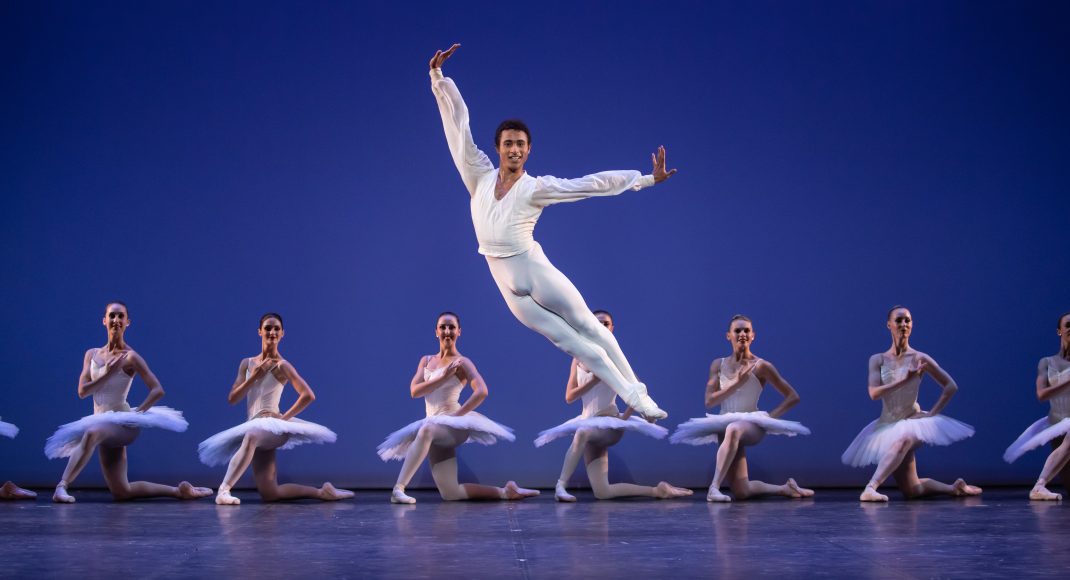
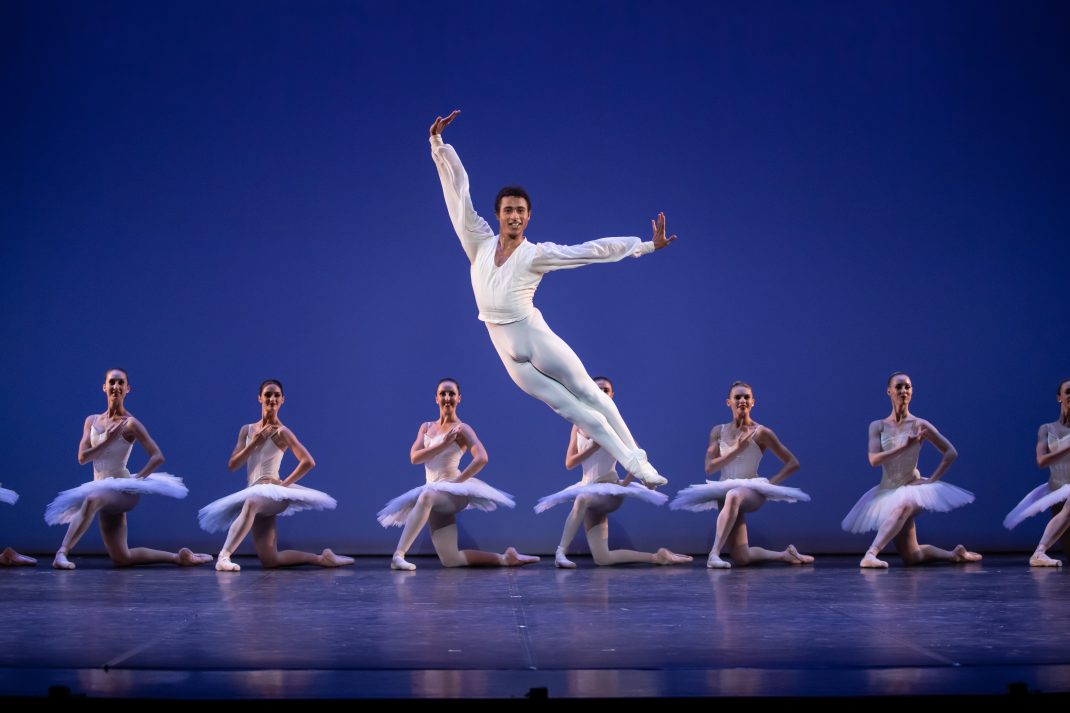
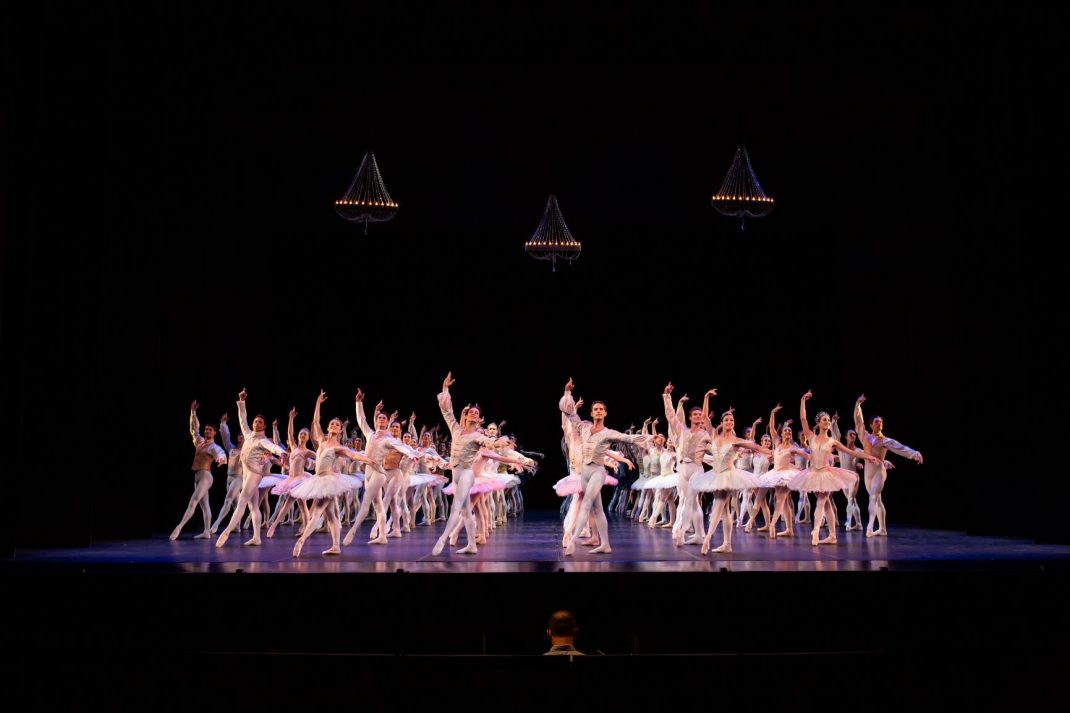
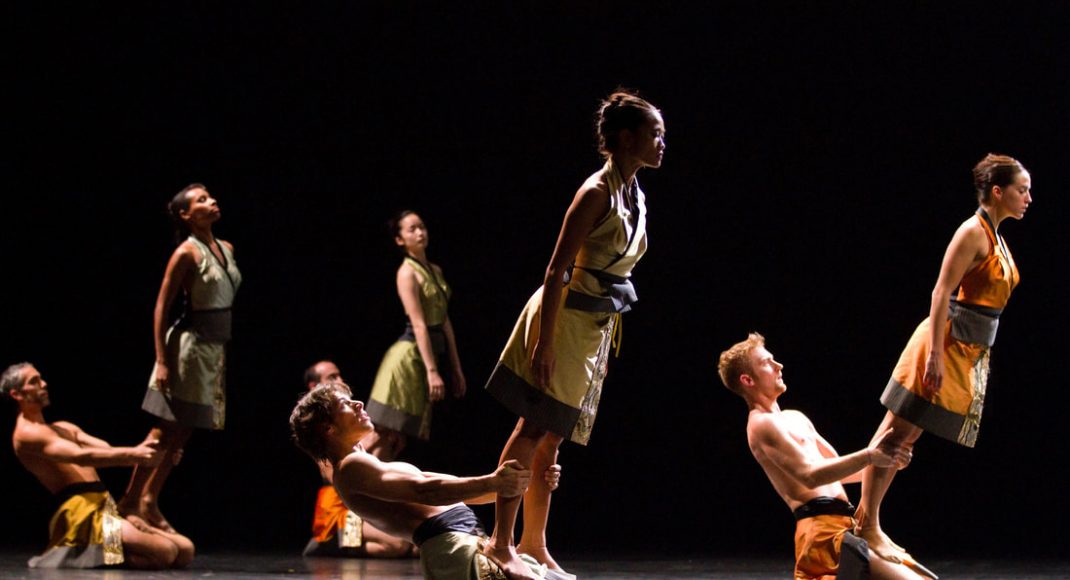
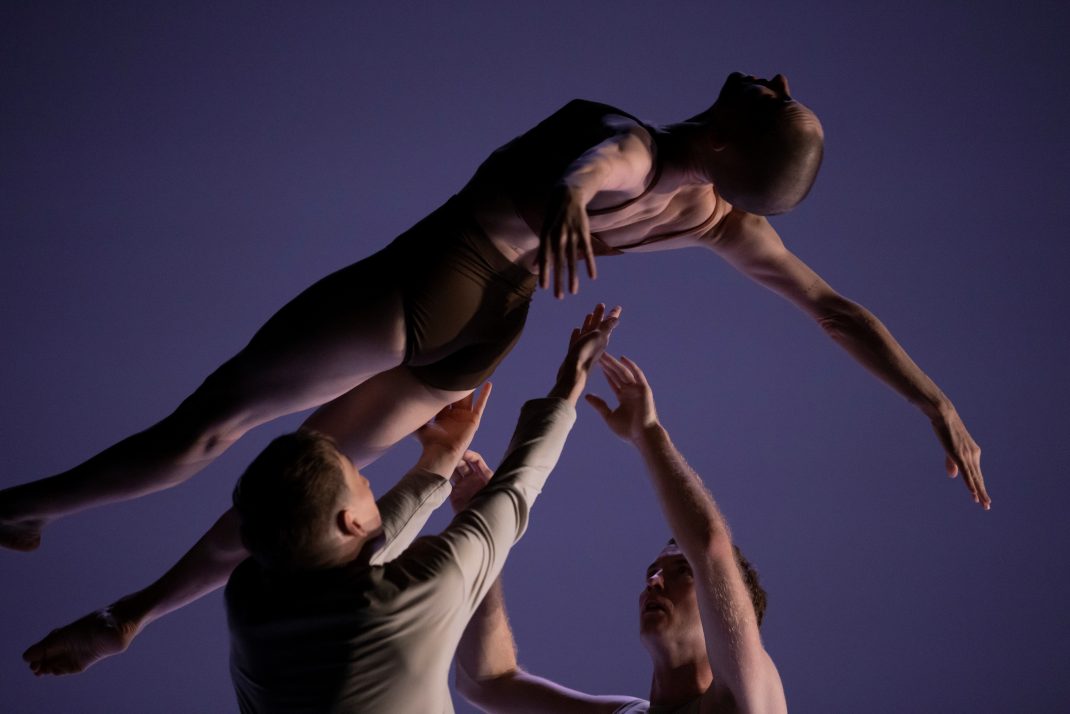
The Four Temperaments was beautifully danced. Some of Balanchine’s vocabulary in this work might also be called quirky but its flow and role in the overall piece was arresting rather than seeming out of place. There is a coherence there.
The Sydney Opera House was making an exceptional effort with its COVID plan, even though the venue was pretty much at 100% capacity. But one aspect of it all was exceptionally annoying. Cast sheets were not available so it was not always possible to identify the performers with accuracy (and so I have not mentioned any names in this review). There was the option to scan a cast list onto one’s phone but how would that list look on a screen the size of a phone, apart from the fact that there is nothing more annoying than audience members looking at their phones during a performance. At least there could have been a cast sheet affixed to a board somewhere in the foyer. Next time I guess I need to print off a cast list from the Australian Ballet’s website and trust that it will be accurate on the day? Perhaps we could have been warned in advance? Or did I miss something along the line?
Michelle Potter, 20 April 2021
Featured image: Dancers of the Australian Ballet in a moment from The Four Temperaments, 2021. Photo: © Daniel Boud